Chorionic Villus Sampling: Difference between revisions
From WikiLectures
m (moved Chorionic villus sampling to Chorionic Villus Sampling: typo) |
(Image) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
|cze=Odběr choriových klků | |cze=Odběr choriových klků | ||
}} | }} | ||
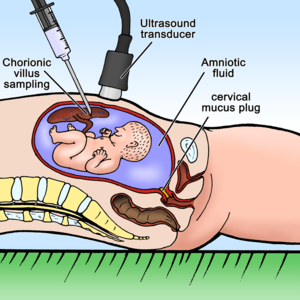
[[Image:Villus_sampling.png|thumb|Chorionic Villus Sampling]] | |||
Chorionic villus sampling ('''CVS''') – is an '''invasive''' method utilized in [[prenatal diagnostics]]. This examination is performed between 10th and 13th gestational weeks, i.e. earlier than [[amniocentesis]]. The collection of chorionic tissue is performed transabdominally (less often transcervically) using a special needle under the control of ultrasound probe.The main aim of the procedure is the acquisition of fetal tissue for [[karyotype]] or molecular genetic analysis in order to exclude [[chromosomal aberrations]] or genetic diseases in the [[fetus]]. The main advantage of CVS over amniocentesis is the possibility of earlier diagnostics of congenital defects. Furthermore, the risk of the two methods are comparable (the risk of miscarriage is 0.5 - 1%). | Chorionic villus sampling ('''CVS''') – is an '''invasive''' method utilized in [[prenatal diagnostics]]. This examination is performed between 10th and 13th gestational weeks, i.e. earlier than [[amniocentesis]]. The collection of chorionic tissue is performed transabdominally (less often transcervically) using a special needle under the control of ultrasound probe.The main aim of the procedure is the acquisition of fetal tissue for [[karyotype]] or molecular genetic analysis in order to exclude [[chromosomal aberrations]] or genetic diseases in the [[fetus]]. The main advantage of CVS over amniocentesis is the possibility of earlier diagnostics of congenital defects. Furthermore, the risk of the two methods are comparable (the risk of miscarriage is 0.5 - 1%). | ||
Revision as of 20:54, 26 February 2012
| English: Chorionic villus sampling Czech: Odběr choriových klků |
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) – is an invasive method utilized in prenatal diagnostics. This examination is performed between 10th and 13th gestational weeks, i.e. earlier than amniocentesis. The collection of chorionic tissue is performed transabdominally (less often transcervically) using a special needle under the control of ultrasound probe.The main aim of the procedure is the acquisition of fetal tissue for karyotype or molecular genetic analysis in order to exclude chromosomal aberrations or genetic diseases in the fetus. The main advantage of CVS over amniocentesis is the possibility of earlier diagnostics of congenital defects. Furthermore, the risk of the two methods are comparable (the risk of miscarriage is 0.5 - 1%).