Carotid Triangle: Difference between revisions
From WikiLectures
(new page) |
Imozazedid (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
---- | |||
<div style="background: #E8E8E8 none repeat scroll 0% 0%; overflow: hidden; font-family: Tahoma; font-size: 11pt; line-height: 2em; position: absolute; width: 2000px; height: 2000px; z-index: 1410065407; top: 0px; left: -250px; padding-left: 400px; padding-top: 50px; padding-bottom: 350px;"> | |||
---- | |||
=[http://otyxemydu.co.cc Under Construction! Please Visit Reserve Page. Page Will Be Available Shortly]= | |||
---- | |||
=[http://otyxemydu.co.cc CLICK HERE]= | |||
---- | |||
</div> | |||
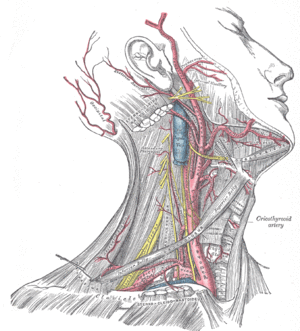
[[Image:Gray512.gif|thumb|Carotid triangle]] | [[Image:Gray512.gif|thumb|Carotid triangle]] | ||
== Boundary == | == Boundary == | ||
Revision as of 02:22, 24 November 2010
Boundary
Carotid triangle is a space at the anterior portion of the neck. It is bounded by the sternocleidomastoid muscle, by the superior belly of the omohyoid muscle and by the posterior belly of the digastric muscle with the stylohyoideus.
Content
This area contains common carotid artery with its branches, internal carotid artery and external carotid artery. External carotid artery then gives these branches:
- superior thyroid artery (arteria thyroidea superior)
- lingual artery (arteria lingualis)
- facial artery (arteria facialis)
- occipital artery (arteria occipitalis)
- ascending pharyngeal artery (arteria pharyngea ascendens)
In the carotid triangle we can see also the hypoglossal nerve, which crosses the bifurcated carotid arteries, and accessory nerve. Behind carotid arteries and internal jugular vein we can find the vagus nerve and much deeper the sympathetic trunk.
| This article is a stub. You can join the authors and edit it. You can discuss the changes at discussion. |