Glucose: Difference between revisions
From WikiLectures
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
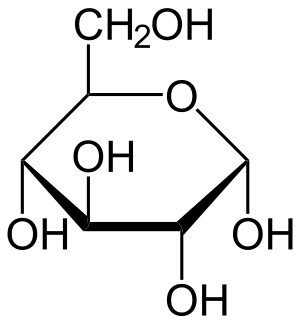
[[File:Alpha-D-Glucopyranose.svg|thumb|α-D-glucopyranose]] | |||
==Characteristics== | ==Characteristics== | ||
D-glucose is the most important naturally occurring [[monosaccharide]] . The structure is a [[hexose]] and an [[aldose]] . It plays an important role especially in energy [[metabolism]] . Major metabolic pathways involving glucose and its derivatives include [[Glycolysis wrong source|glycolysis]] , [[gluconeogenesis]] , [[glycogen]] synthesis and degradation , and the [[pentose cycle]] . | D-glucose is the most important naturally occurring [[monosaccharide]] . The structure is a [[hexose]] and an [[aldose]] . It plays an important role especially in energy [[metabolism]] . Major metabolic pathways involving glucose and its derivatives include [[Glycolysis wrong source|glycolysis]] , [[gluconeogenesis]] , [[glycogen]] synthesis and degradation , and the [[pentose cycle]] . | ||
==Links== | ==Links== | ||
Revision as of 01:08, 20 November 2022
Characteristics
D-glucose is the most important naturally occurring monosaccharide . The structure is a hexose and an aldose . It plays an important role especially in energy metabolism . Major metabolic pathways involving glucose and its derivatives include glycolysis , gluconeogenesis , glycogen synthesis and degradation , and the pentose cycle .
Links
Related Articles
References
- MATOUŠ, Bohuslav, et al. Fundamentals of medical chemistry and biochemistry. 1st edition. Prague: Galén, 2010. 540 pp. ISBN 978-80-7262-702-8 .File:D-glucose fischer 0.pngD-glucose, Fischer projection