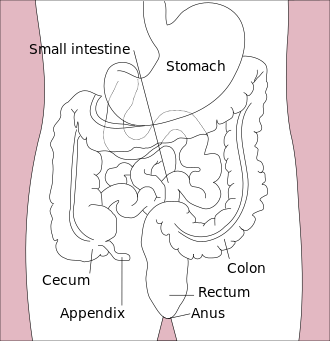
Small and large intestine: Difference between revisions
(Original text was from Wikiscripta: Tenké a tlusté střevo (https://www.wikiskripta.eu/index.php?curid=38749)) |
No edit summary |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== | == Small intestine == | ||
{{ | {{Details|Small intestine}} | ||
The small intestine, ''intestinum tenue'' , connects to the stomach as a tube with a length of 5-7 m and a width of 3-4 cm . The main functions of the small intestine include [[trávení|digestion]] and absorption. | |||
Sections of the small intestine: | |||
* [[duodenum]] | * [[duodenum]] | ||
* jejunum | * jejunum | ||
* ileum | * ileum | ||
[[File:Stomach colon rectum diagram-en.svg|thumb|Diagram of the small and large intestine]] | |||
=== Mucous membrane === | |||
'''plicae circulares, transverse eyelashes''' | |||
* perpendicular to the longitudinal axis | |||
*6-8 mm high | |||
*formed only in the duodenum and jejunum | |||
*fixed (arising from adhesion of the submucosa) | |||
*they decrease towards the ileum | |||
'''villi (villi intestinales)''' | |||
* mucous growths | |||
*0.3-1 mm | |||
*towards the ileum, they decrease and their density decreases | |||
*at the base of the villi the mouths of Lieberkühn's crypts (tubes running vertically through the mucosaPaneth cells line the bottom) | |||
==== Epithelium ==== | |||
It covers both villi and Lieberkühn's crypts (except the bottom). | |||
'''Enterocytes''' | |||
''' | Significantly participates in resorpc. They are cylindrical, have an ovoid core in the lower third. At the apex is an annealed cuticle made of microvilli. The lifespan of enterocytes is about 1–3 days (part of faeces). They are renewed again by the [[Mitotické dělení|mitotic activity of the]] enterocytes of the Lieberkühn crypts. | ||
[[File:Small intestine low mag.jpg|thumb|Microscopic image of the mucosa of the small intestine (HE staining)]] | |||
'''Goblet cells''' | |||
Goblet cells are club-shaped and bright. It is found on the keys and in the crypts. In the extension of the apex of the [[Mucinózní buňka|mucin]] grain. | |||
''' | '''Paneth cells''' | ||
They have a conical shape. Apex [[Barvení hematoxylin-eosin|eosinophilic]] (secretion of peptidases, lysozyme enzyme – antimicrobial). | |||
''' | '''Endocrine cells''' | ||
Endocrine cells are enterochromaffin, A-cells. | |||
==== Lamina propria ==== | ==== Lamina propria ==== | ||
It is made up of sparse collagen tissue. There are lymph nodes in it. Forms villi - in the axis of the villus a lymphatic capillary (chylo vessel) + 2 arterioles. | |||
==== Lamina muscularis mucosae ==== | ==== Lamina muscularis mucosae ==== | ||
Hairpins <math>\rightarrow</math> contraction empties the chyle vessel. | |||
=== Duodenum === | === Duodenum === | ||
This is the initial and at the same time the shortest section of the small intestine. It is 20-28 cm long . There are no plicae circulares (transverse folds) in the duodenum, they start from the papilla duodeni major. It contains few goblet cells. Submucosa up to [[Duodenum|papilla duodeni major]] penetrated by ''Brunner's glands''. | |||
Brunner's glands | |||
:- | :- branched, mucinous (alkaline secretion) | ||
:- | :- only septa form ligaments | ||
:- | :- they also extend into the lamina propria mucosae | ||
:- | :- opening at the bottom of the Lieberkühn crypts | ||
=== Jejunum === | === Jejunum === | ||
The jejunum has long finger-like villi, which are usually cut transversely on the specimen. Many goblet cells and lymphatic follicles are also found here. In the mucosa of the jejunum, we find only noduli (folliculi) lymphatici solitarii. At the same time, the jejunum is very well penetrated by a rich vascular supply. | |||
=== Ileum === | === Ileum === | ||
It has low plicae circulares and is completely absent in the final section. Low villi are also found in the ileum. In the [[lamina propria mucosae]] (tunica mucosa) we find many lymphatic follicles that cluster and form '''Peyer's patches''' . | |||
== Colon == | |||
{{Details|Colon}} | |||
The large intestine is connected to the small intestine. The length of the large intestine is 1.2-1.5 m , the width is about '''4-7.5 cm''' . Major functions include resorption of water and [[chemická rovnováha|electrolytes]]. Furthermore, the large intestine removes unabsorbed waste as faeces. | |||
=== | Sections of the large intestine: | ||
* | * caecum with appendix vermiformis | ||
* | *colon ascends[[File:Blausen 0603 LargeIntestine Anatomy.png|thumb|Anatomy of the large intestine]] | ||
:* | *transversus | ||
:* | *descending | ||
*sigmoid | |||
*rectum | |||
=== Structure === | |||
* there are no plicae circulares and villi | |||
*slender and deep Leiberkühn crypts | |||
:* from enterocytes and goblet cells (they predominate!) | |||
:*they are not Paneth cells | |||
=== Appendix | === Vermiform Appendix === | ||
The length of the appendix is '''5–10 cm''' , diameter '''0.8 cm''' . Here we find shallow Lieberkühn crypts, where goblet cells predominate. In the lamina propria mucosae there are many confluent lymph nodes with germinal centers. The lamina muscularis mucosae is sometimes absent. The appendix has a thin continuous tunica muscularis externa and a tunica serosa. | |||
=== Caecum | === Caecum and colon === | ||
The outer layer of the tunica muscularis consists of only 3 stripes (taeniae coli). Serous outgrowths - appendices epiploicae. The back wall of the colon is covered with adventitia. | |||
=== Rectum === | === Rectum === | ||
'''''Pars ampullaris''''' | '''''Pars ampullaris''''' | ||
* | * structure like colon, but there are many lymphocytes in the mucosa and submucosa and the outer muscle is continuous | ||
'''''Canalis analis | '''''Canalis analis'' 3 sections''' | ||
* '''hemorrhoidal zone''' | |||
* ''' | - region of columnae, sinus and recessus anales - sharp transition from cylindrical to squamous epithelium - lamina muscularis mucosae is missing - venous plexus in the submucosa | ||
- | |||
- | |||
- | |||
- | |||
* ''' | * '''intermediate zone''' | ||
- | - above the smooth muscle of the sphincter ani internus (reinforced tunica muscularis) - squamous epithelium - in the lamina propria of Vater-Pacini bodies and [[Kožní adnexa|sebaceous glands.]] | ||
- | |||
- | |||
* '''zona cutanea''' | * '''zona cutanea''' | ||
- | - structure like skin (hair, glands) - around the anal opening the sphincter ani externus muscle (transverse striated) | ||
- | |||
== Links == | |||
== | === Related Articles === | ||
=== | *[[Tenké střevo|Small intestine]] | ||
*[[Tenké střevo]] | |||
*[[Tlusté střevo]] | *[[Tlusté střevo|Colon]] | ||
*[[Duodenum]] | *[[Duodenum]] | ||
*[[Tenké střevo (preparát)]] | *[[Tenké střevo (preparát)|Small intestine (preparation)]] | ||
*[[Tlusté střevo (preparát)]] | *[[Tlusté střevo (preparát)|Colon (preparation)]] | ||
*[[Duodenum (obrázek)|Duodenum ( | *[[Duodenum (obrázek)|Duodenum (preparation)]] | ||
''' | '''Practicing histological preparations''' | ||
* [[Procvičování:Trávicí systém]] | * [[Procvičování:Trávicí systém|Excercise: Digestive system]] | ||
=== | === Source === | ||
*{{ | *{{Cite | ||
| | | type = lecture | ||
| | | surname = Jarkovská | ||
| | | name = Daniela | ||
| | | topic = Trávicí systém | ||
| | | subject = Histologie a embryologie | ||
| | | specialization = Zubní lékařství, Všeobecné lékařství | ||
| | | faculty = 1. lékařská fakulta | ||
| | | university = Univerzita Karlova | ||
| | | location = Praha | ||
| | | date = 26.10.2011 | ||
}} | }} | ||
=== | === References === | ||
*{{ | *{{Cite | ||
| | | type = book | ||
| isbn = 80-86022-80-3 | | isbn = 80-86022-80-3 | ||
| | | surname1 = Konrádová | ||
| | | name1 = Václava | ||
| | | surname2 = Uhlík | ||
| | | name2 = Jiří | ||
| | | surname3 = Vajner | ||
| | | name3 = Luděk | ||
| | | title = Funkční histologie | ||
| | | edition = 2 | ||
| | | location = Jinočany | ||
| | | publisher = H & H | ||
| | | year = 2000 | ||
| | | range = 291 | ||
}} | }} | ||
* {{ | * {{Cite | ||
| | | type = book | ||
| isbn = 80-247-0143-X | | isbn = 80-247-0143-X | ||
| | | surname1 = Čihák | ||
| | | name1 = Radomír | ||
| | | surname2 = Grim | ||
| | | name2 = Miloš | ||
| | | title = Anatomie. 2 | ||
| | | edition = 2 | ||
| | | location = Praha | ||
| | | publisher = Grada Publishing | ||
| | | year = 2002 | ||
}} | }} | ||
</noinclude> | </noinclude> | ||
[[ | [[Category:Histology]] | ||
[[ | [[Category:Anatomy]] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:02, 24 January 2023
Small intestine[edit | edit source]
The small intestine, intestinum tenue , connects to the stomach as a tube with a length of 5-7 m and a width of 3-4 cm . The main functions of the small intestine include digestion and absorption.
Sections of the small intestine:
- duodenum
- jejunum
- ileum
Mucous membrane[edit | edit source]
plicae circulares, transverse eyelashes
- perpendicular to the longitudinal axis
- 6-8 mm high
- formed only in the duodenum and jejunum
- fixed (arising from adhesion of the submucosa)
- they decrease towards the ileum
villi (villi intestinales)
- mucous growths
- 0.3-1 mm
- towards the ileum, they decrease and their density decreases
- at the base of the villi the mouths of Lieberkühn's crypts (tubes running vertically through the mucosaPaneth cells line the bottom)
Epithelium[edit | edit source]
It covers both villi and Lieberkühn's crypts (except the bottom).
Enterocytes
Significantly participates in resorpc. They are cylindrical, have an ovoid core in the lower third. At the apex is an annealed cuticle made of microvilli. The lifespan of enterocytes is about 1–3 days (part of faeces). They are renewed again by the mitotic activity of the enterocytes of the Lieberkühn crypts.
Goblet cells
Goblet cells are club-shaped and bright. It is found on the keys and in the crypts. In the extension of the apex of the mucin grain.
Paneth cells
They have a conical shape. Apex eosinophilic (secretion of peptidases, lysozyme enzyme – antimicrobial).
Endocrine cells
Endocrine cells are enterochromaffin, A-cells.
Lamina propria[edit | edit source]
It is made up of sparse collagen tissue. There are lymph nodes in it. Forms villi - in the axis of the villus a lymphatic capillary (chylo vessel) + 2 arterioles.
Lamina muscularis mucosae[edit | edit source]
Hairpins contraction empties the chyle vessel.
Duodenum[edit | edit source]
This is the initial and at the same time the shortest section of the small intestine. It is 20-28 cm long . There are no plicae circulares (transverse folds) in the duodenum, they start from the papilla duodeni major. It contains few goblet cells. Submucosa up to papilla duodeni major penetrated by Brunner's glands.
Brunner's glands
- - branched, mucinous (alkaline secretion)
- - only septa form ligaments
- - they also extend into the lamina propria mucosae
- - opening at the bottom of the Lieberkühn crypts
Jejunum[edit | edit source]
The jejunum has long finger-like villi, which are usually cut transversely on the specimen. Many goblet cells and lymphatic follicles are also found here. In the mucosa of the jejunum, we find only noduli (folliculi) lymphatici solitarii. At the same time, the jejunum is very well penetrated by a rich vascular supply.
Ileum[edit | edit source]
It has low plicae circulares and is completely absent in the final section. Low villi are also found in the ileum. In the lamina propria mucosae (tunica mucosa) we find many lymphatic follicles that cluster and form Peyer's patches .
Colon[edit | edit source]
The large intestine is connected to the small intestine. The length of the large intestine is 1.2-1.5 m , the width is about 4-7.5 cm . Major functions include resorption of water and electrolytes. Furthermore, the large intestine removes unabsorbed waste as faeces.
Sections of the large intestine:
- caecum with appendix vermiformis
- colon ascends
- transversus
- descending
- sigmoid
- rectum
Structure[edit | edit source]
- there are no plicae circulares and villi
- slender and deep Leiberkühn crypts
- from enterocytes and goblet cells (they predominate!)
- they are not Paneth cells
Vermiform Appendix[edit | edit source]
The length of the appendix is 5–10 cm , diameter 0.8 cm . Here we find shallow Lieberkühn crypts, where goblet cells predominate. In the lamina propria mucosae there are many confluent lymph nodes with germinal centers. The lamina muscularis mucosae is sometimes absent. The appendix has a thin continuous tunica muscularis externa and a tunica serosa.
Caecum and colon[edit | edit source]
The outer layer of the tunica muscularis consists of only 3 stripes (taeniae coli). Serous outgrowths - appendices epiploicae. The back wall of the colon is covered with adventitia.
Rectum[edit | edit source]
Pars ampullaris
- structure like colon, but there are many lymphocytes in the mucosa and submucosa and the outer muscle is continuous
Canalis analis 3 sections
- hemorrhoidal zone
- region of columnae, sinus and recessus anales - sharp transition from cylindrical to squamous epithelium - lamina muscularis mucosae is missing - venous plexus in the submucosa
- intermediate zone
- above the smooth muscle of the sphincter ani internus (reinforced tunica muscularis) - squamous epithelium - in the lamina propria of Vater-Pacini bodies and sebaceous glands.
- zona cutanea
- structure like skin (hair, glands) - around the anal opening the sphincter ani externus muscle (transverse striated)
Links[edit | edit source]
Related Articles[edit | edit source]
Practicing histological preparations
Source[edit | edit source]
- JARKOVSKÁ, Daniela. Trávicí systém [lecture for subject Histologie a embryologie, specialization Zubní lékařství, Všeobecné lékařství, 1. lékařská fakulta Univerzita Karlova]. Praha. 26.10.2011.
References[edit | edit source]
- KONRÁDOVÁ, Václava – UHLÍK, Jiří – VAJNER, Luděk. Funkční histologie. 2. edition. Jinočany : H & H, 2000. 291 pp. ISBN 80-86022-80-3.
- ČIHÁK, Radomír – GRIM, Miloš. Anatomie. 2. 2. edition. Praha : Grada Publishing, 2002. ISBN 80-247-0143-X.