Amino Acids (FBLT): Difference between revisions
From WikiLectures
Belkis Cokan (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
S.Filonova (talk | contribs) m (checked by editor) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
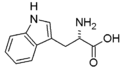
'''Amino acids''' are the basic structural component of proteins and peptides. They contain at least one '''amino'''- (–NH 2) and one '''carboxyl''' (–COOH) group. | |||
'''Amino acids''' are the basic structural component of proteins and peptides . They contain at least one '''amino'''- (–NH 2 ) and one '''carboxyl''' (–COOH) group. | |||
From the point of view of biosynthesis, we can divide them into: | From the point of view of biosynthesis, we can divide them into: | ||
# '''Non-essential''' , which the body can synthesize: Gly, Ala, Pro, Ser, Tyr, Cys, Asp, Asn, Glu, Gln | # '''Non-essential''', which the body can synthesize: Gly, Ala, Pro, Ser, Tyr, Cys, Asp, Asn, Glu, Gln | ||
# '''Essential''' , which we must take in food | # '''Essential''', which we must take in food | ||
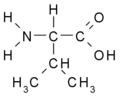
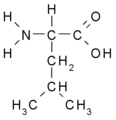
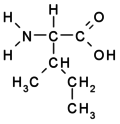
::* '''branched''': Val, Leu, Ile | ::* '''branched''': Val, Leu, Ile | ||
| Line 45: | Line 32: | ||
<center><gallery perrow="5"> | <center><gallery perrow="5"> | ||
File:Threonine.png|thumb|Threonine | File:Threonine.png|thumb|Threonine | ||
</gallery></center> | </gallery></center> | ||
{{Details | Amino acids}} | {{Details | Amino acids}} | ||
Latest revision as of 18:20, 23 March 2023
Amino acids are the basic structural component of proteins and peptides. They contain at least one amino- (–NH 2) and one carboxyl (–COOH) group.
From the point of view of biosynthesis, we can divide them into:
- Non-essential, which the body can synthesize: Gly, Ala, Pro, Ser, Tyr, Cys, Asp, Asn, Glu, Gln
- Essential, which we must take in food
- branched: Val, Leu, Ile
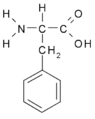
- aromatic: Phe, Trp
- basic (basic): His and Arg (both essential only in childhood or in critical states), Lys
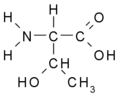
- with sulfur content: Met
- with OH− group: Thr