Orthopantomography: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Jakubkvasnak (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
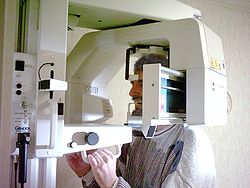
Orthopantomography is a radiodiagnostic method using [[RTG]] rays. Its result is an orthopantomogram (OPG) - a picture showing both jaws, dentition, jaw joints, jaw cavities and nasal cavity. This method is mainly used in dentistry. It belongs to extraoral imaging methods. | Orthopantomography is a radiodiagnostic method using [[RTG]] rays. Its result is an orthopantomogram (OPG) - a picture showing both jaws, dentition, jaw joints, jaw cavities and nasal cavity. This method is mainly used in dentistry. It belongs to extraoral imaging methods. | ||
== Imaging Technique == | == Imaging Technique == | ||
The technique is based on the combined rotational and translational movement of the X-ray tube and film and the screening of the rays by a vertical slit diaphragm.<ref name="Sponge">{{ | The technique is based on the combined rotational and translational movement of the X-ray tube and film and the screening of the rays by a vertical slit diaphragm.<ref name="Sponge">{{Cite| type = book| isbn = 80-246-0005-6| surname1 = Mushroom| name1 = Robert| surname2 = Kreuzberg| name2 = Boris| surname3 = Zemen| name3 = George| surname4 = Zicha| name4 = Antonín| title = Basics of radiodiagnostics and other imaging methods in dentistry| edition = 1| location = Prague| publisher = Karolinum| year = 1999}}</ref> | ||
* '''Exposure''' approx. 15 s. | * '''Exposure''' approx. 15 s. | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
During imaging, the patient's head is fixed in a cephalostat with the mouth slightly ajar. The X-ray and the film move in sync around the patient's head so that the resulting image is orthoradial. | During imaging, the patient's head is fixed in a cephalostat with the mouth slightly ajar. The X-ray and the film move in sync around the patient's head so that the resulting image is orthoradial. | ||
== [[Ortopantomogram]] == | == [[Ortopantomogram]] == | ||
{{Edit article|Ortopantomogram}}{{:Ortopantomogram}} | {{Edit article|Ortopantomogram}}<!------------------------------------------------ -------------------------------------------------- -------------- | ||
* EMBEDDED ARTICLE | |||
* Attention - this article is used by other articles in which it is inserted. Please be careful when editing it: | |||
* 1. Do not delete <noinclude> </noinclude> statements. They indicate the parts of the article that are not transferred when pasted. | |||
* 2. Do not change the levels of the headings used. Injudicious use of top-level headings could make other articles confusing. | |||
* 3. More extensive editing, expansion or shortening of the article could disrupt the concept of other articles. Discuss the changes in the discussion. | |||
* For a list of articles in which this article is embedded, see the list of linking articles under the "Links Here" link. | |||
* | |||
* Please do not delete this comment. In case of confusion, contact the editors (redakce@wikiskripta.eu) | |||
* | |||
* This notice is inserted with the template {{subst:Embedded article}} | |||
-------------------------------------------------- -------------------------------------------------- ---------->[[File:Wechselgebiss1.jpg|thumb|200px|Ortopantomogram of mixed dentition]][[File:Ortopantomogram description.jpg|thumb|200px|OPG with description of basic structures]]'''Orthopantomogram''' is a clear panoramic [[x-ray]] image capturing the dentition, both jaws, jaw joints, part of the nasal cavity and part of the maxillary cavity of the subject. It is obtained by [[ortopantomography|orthopantomographic imaging technique]]. The image consists of two lateral and one back-front image, i.e. three images in total (hence the sometimes designation '''sonogram''', i.e. an image of three zones) - it is actually a modified [[tomogram]]. The first OPG was carried out in 1959 in Helsinki, it became common practice in the 1980s. It is now one of the main imaging methods in dentistry. It should be performed at every entrance examination, then once every 2-5 years as a preventive measure, depending on the state of dental hygiene. | |||
* A classic OPG image has dimensions of '''15 cm × 30 cm'''', sometimes 30 cm × 12 cm. | |||
*All structures are slightly magnified on OPG (1.25–1.35×). | |||
* Exposure time is approximately 15 seconds. | |||
*The patient's head is stabilized thanks to the '''cephalostat''''. | |||
*Camper's line is parallel to the ground. | |||
*The vest does, but the collar doesn't - it would cause artifacts. | |||
===Benefits=== | |||
The main advantage of OPG is the fact that the situation in both jaws and surrounding structures is captured in one image. The fact that the image is taken at the same time reduces the [[radiation load]] quite a bit - to show the situation in both jaws, we would need at least 6 images with [[Bite wing|bite-wing]], and even then we would not have a large overview, a minimum of 14 images would be needed for an apical projection. One OPG is equivalent to approximately four intraoral images. | |||
===Disadvantages=== | |||
The disadvantage of OPG is a certain degree of distortion, a typical OPG is approximately 1.25x magnified, summations occur, and when performed poorly we often encounter ''"burn-out effects"''. The deformation of the image is pronounced in the frontal part and the angle of the mandible. Another disadvantage is that it is relatively difficult to take this picture with children, due to poor cooperation. | |||
===Use in diagnostics=== | |||
*[[Dental caries]]s (depending on image quality), | |||
*Periapical pathology, | |||
*[[cyst|Cysts]], | |||
*[[Radices relictae]], | |||
*[[Tumor]]s, | |||
*Retined/semi-retined teeth, | |||
*[[fracture|Fractures]], | |||
*Bone resorption (periodontology), | |||
*Some disorders [[Articulatio temporomandibularis|TMK]], | |||
*Foreign bodies in the jaw cavity (partially). | |||
<noinclude>{{:Ortopantomogram}} | |||
== X-ray conditions == | == X-ray conditions == | ||
=== Head position === | === Head position === | ||
In order to obtain a high-quality image, the patient's head must be fixed in the '''cephalostat'''' under the following conditions: | In order to obtain a high-quality image, the patient's head must be fixed in the '''cephalostat'''' under the following conditions: | ||
| Line 43: | Line 74: | ||
* {{Cite | * {{Cite | ||
| type = book | | type = book | ||
| | | isbn = 80-246-0005-6 | ||
| | | surname1 = HOUBA | ||
| | | name1 = Robert | ||
| | | surname2 = KREUZBERG | ||
| | | name2 = Boris | ||
| surname3 = ZEMEN | |||
| name3 = Jiří | |||
| title = Basics of radiodiagnostics and other imaging methods in dentistry | | title = Basics of radiodiagnostics and other imaging methods in dentistry | ||
| edition = | | edition = 1 | ||
| location = Prague | | location = Prague | ||
| publisher = Karolinum | | publisher = Karolinum | ||
Latest revision as of 12:40, 26 November 2023
Orthopantomography is a radiodiagnostic method using RTG rays. Its result is an orthopantomogram (OPG) - a picture showing both jaws, dentition, jaw joints, jaw cavities and nasal cavity. This method is mainly used in dentistry. It belongs to extraoral imaging methods.
Imaging Technique
The technique is based on the combined rotational and translational movement of the X-ray tube and film and the screening of the rays by a vertical slit diaphragm.[1]
- Exposure approx. 15 s.
- Voltage: 55-85 kV.
- Current: 2-30mA.
During imaging, the patient's head is fixed in a cephalostat with the mouth slightly ajar. The X-ray and the film move in sync around the patient's head so that the resulting image is orthoradial.
Ortopantomogram
Orthopantomogram is a clear panoramic x-ray image capturing the dentition, both jaws, jaw joints, part of the nasal cavity and part of the maxillary cavity of the subject. It is obtained by orthopantomographic imaging technique. The image consists of two lateral and one back-front image, i.e. three images in total (hence the sometimes designation sonogram, i.e. an image of three zones) - it is actually a modified tomogram. The first OPG was carried out in 1959 in Helsinki, it became common practice in the 1980s. It is now one of the main imaging methods in dentistry. It should be performed at every entrance examination, then once every 2-5 years as a preventive measure, depending on the state of dental hygiene.
- A classic OPG image has dimensions of 15 cm × 30 cm', sometimes 30 cm × 12 cm.
- All structures are slightly magnified on OPG (1.25–1.35×).
- Exposure time is approximately 15 seconds.
- The patient's head is stabilized thanks to the cephalostat'.
- Camper's line is parallel to the ground.
- The vest does, but the collar doesn't - it would cause artifacts.
Benefits
The main advantage of OPG is the fact that the situation in both jaws and surrounding structures is captured in one image. The fact that the image is taken at the same time reduces the radiation load quite a bit - to show the situation in both jaws, we would need at least 6 images with bite-wing, and even then we would not have a large overview, a minimum of 14 images would be needed for an apical projection. One OPG is equivalent to approximately four intraoral images.
Disadvantages
The disadvantage of OPG is a certain degree of distortion, a typical OPG is approximately 1.25x magnified, summations occur, and when performed poorly we often encounter "burn-out effects". The deformation of the image is pronounced in the frontal part and the angle of the mandible. Another disadvantage is that it is relatively difficult to take this picture with children, due to poor cooperation.
Use in diagnostics
- Dental cariess (depending on image quality),
- Periapical pathology,
- Cysts,
- Radices relictae,
- Tumors,
- Retined/semi-retined teeth,
- Fractures,
- Bone resorption (periodontology),
- Some disorders TMK,
- Foreign bodies in the jaw cavity (partially).
X-ray conditions
Head position
In order to obtain a high-quality image, the patient's head must be fixed in the cephalostat' under the following conditions:
- Camper's line is parallel to the ground,
- Head position is centered,
- The front teeth are in the focus zone of the device.
Today's devices have a light system that "navigates" to the correct fixation of the head.
Benefits of OPG
- Simplicity,
- An overview of dentition, jawbones and joints in a single image,
- 90% less surface radiation dose[1] compared to X-ray status (10 intraoral images),
- Option to compare right and left sides.
Disadvantages of OPG
- Shading of the frontal sections of the jaw of the spine – today the sensitivity in this section is automatically increased to improve the quality,
- Hypermetric image - magnification factor is 1.2-1.35.[2]
Links
Related Articles
References
- HOUBA, Robert – KREUZBERG, Boris – ZEMEN, Jiří. Basics of radiodiagnostics and other imaging methods in dentistry. 1. edition. Prague : Karolinum, 1999. 500 pp. vol. 1. ISBN 80-246-0005-6.
- ↑ Jump up to: a b MUSHROOM, Robert – KREUZBERG, Boris – ZEMEN, George. Basics of radiodiagnostics and other imaging methods in dentistry. 1. edition. Prague : Karolinum, 1999. ISBN 80-246-0005-6.
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedMushroom