Angelman Syndrome: Difference between revisions
From WikiLectures
(new dictionary, text was extracted from Genomic Imprinting, author is Garasone) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<!---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
* INSERTED ARTICLE | |||
* Warning – this article is used in other articles where it is inserted. If you are changing this article, you are changing other articles at the same moment. Please, be careful when you are editing it: | |||
* 1. Do not remove commands <noinclude> </noinclude>. These command usually mark which are not used in other articles, where is this article used. | |||
* 2. Do not change level of headings. | |||
* 3. Great expansion or removing of the text of the article can change the meaning of other articles. You can discuss all these changes on discussion page of this article. | |||
* All the articles, where is this article inserted can be found in ''Toolbox'' → ''What links here''. | |||
* | |||
* Please, do not remove this comment. If you are not sure, you can contact our [[WikiLectures:Editorial board | editorial board]]. | |||
* | |||
* This warning note is automatically inserted by inserting the template {{subst:Inserted article}}. | |||
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------->{{Was checked| 20120114185235 | [[User:OSeda|Ondřej Šeda, MD, PhD]]|9634}} | |||
__NOTOC__<noinclude>{{Dictionary | __NOTOC__<noinclude>{{Dictionary | ||
|eng=Angelman syndrome}}</noinclude> | |eng=Angelman syndrome}}</noinclude> | ||
[[File:Angelman.jpg|thumb|'' | [[File:Angelman.jpg|thumb|''Chromosome 15'' - '''Angelman syndrome''']] | ||
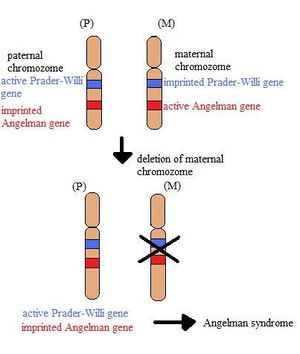
*This syndrome is caused by the | * This syndrome is caused by the '''loss of function of ''[[gene]] UBE3A''''' - physiologically, just the maternal copy of this gene is functional (the paternal copy is imprinted, i.e. [[Epigenetics|epigenetically]] silenced). Thus loss of the maternal gene causes this syndrome. The critical genomic region of this disorder is located on [[chromosome]] 15 (The Prader-Willi/Angelman Critical Region- PWACR; 15q11-q13). This genetic disorder is connected especially with the nervous system. Children are affected in their early age. | ||
*''Typical symptoms'': | * ''Typical symptoms'': severe intellectual disability and developmental delay, speech problems, [[ataxia]], [[epilepsy]] or microcephaly. | ||
* | * Patients are sometimes called "'''happy puppets'''" because of their behavior. They smile frequently, laugh and have flapping movements. | ||
*Incidence of Angelman syndrome is ''1 in 12 000 - 20 000'' people worldwide. | * Incidence of Angelman syndrome is ''1 in 12 000 - 20 000'' people worldwide. | ||
<noinclude> | <noinclude> | ||
== Links == | == Links == | ||
=== Related articles === | === Related articles === | ||
* [[Genomic Imprinting]] | * [[Genomic Imprinting]] | ||
* [[Prader-Willi Syndrome]] | |||
* [[Gene]] | * [[Gene]] | ||
* [[Allele]] | * [[Allele]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Chromosome]] | ||
=== Sources=== | === Sources === | ||
* [http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/handbook/inheritance/updimprinting What are Genomic Imprinting and Uniparental Disomy] | * [http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/handbook/inheritance/updimprinting What are Genomic Imprinting and Uniparental Disomy] | ||
* [http://www.geneimprint.com/site/what-is-imprinting What is Genomic Imprinting?] | * [http://www.geneimprint.com/site/what-is-imprinting What is Genomic Imprinting?] | ||
| Line 28: | Line 42: | ||
</noinclude> | </noinclude> | ||
[[Category: Biology]] | [[Category:Inserted articles]] | ||
[[Category: Genetics]] | [[Category:Biology]] | ||
[[Category:Genetics]] | |||
[[Category:Paediatrics]] | |||
Latest revision as of 10:09, 23 December 2023
| English: Angelman syndrome |
- This syndrome is caused by the loss of function of gene UBE3A - physiologically, just the maternal copy of this gene is functional (the paternal copy is imprinted, i.e. epigenetically silenced). Thus loss of the maternal gene causes this syndrome. The critical genomic region of this disorder is located on chromosome 15 (The Prader-Willi/Angelman Critical Region- PWACR; 15q11-q13). This genetic disorder is connected especially with the nervous system. Children are affected in their early age.
- Typical symptoms: severe intellectual disability and developmental delay, speech problems, ataxia, epilepsy or microcephaly.
- Patients are sometimes called "happy puppets" because of their behavior. They smile frequently, laugh and have flapping movements.
- Incidence of Angelman syndrome is 1 in 12 000 - 20 000 people worldwide.
Links[edit | edit source]
Related articles[edit | edit source]
Sources[edit | edit source]
Bibliography[edit | edit source]
- KUMAR, ABBAS, FAUSTO, MITCHELL,. Robbins Basic Pathology. 8th edition edition. 2007. ISBN 978-0-8089-2366-4.