Extraocular muscles: Difference between revisions
From WikiLectures
Cateducated (talk | contribs) (added categories) |
Darsh jhala (talk | contribs) m (Size change : Extraocular muscles (schematic) - Eshaan Mehmi) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Extraocular muscles (schematic) - Eshaan Mehmi.jpg|thumb|557x557px|Extraocular muscles (schematic) by Eshaan Mehmi]] | |||
There are 7 extra-ocular muscles - 6 of each responsible for moving the eye ball and 1 is responsible for raising the eyelids. | |||
[[File:Function of eye muscles.png|thumb|Function of eye muscles]] | |||
The extra-ocular muscles are: | |||
'''<u>Levator palpebrae Superioris</u>''' (most superior extra-ocular muscle) | |||
* <u>Origin</u>: lesser wing of sphenoid bone (superior-anterior to optic canal) | |||
* <u>Insertion</u>: superior tarsus of the eyelid [[File:Lateral view of Eye muscles.png|thumb|Lateral view of Eye muscles]][[File:Frontal Section.png|thumb|249x249px|Frontal Section]] | |||
* <u>Function</u>: raising the eyelid | |||
* <u>Innervation</u>: superior division of the oculomotor nerve (CN 3). | |||
* <u>Unique feature</u>: some of its inferior fibers are smooth muscle fibers - help with eyelid elevation. Innervated by post-ganglionic sympathetic fibers. | |||
'''<u>Rectus Muscles</u>''' (superior, medial and lateral) | |||
<u>Origin</u>: the common tendinous ring (all of the muscles) | |||
<u>Insertion</u>: sclera (posterior to corneoscleral junction) | |||
<u>Function</u>: the axis of the orbit and the axis of the eyeball aren’t the same | |||
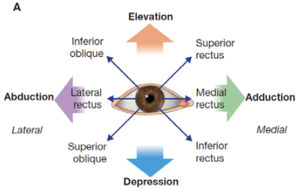
* Superior rectus: moves the eyeball superiorly and medially. | |||
* Inferior rectus: moves the eyeball inferiorly and medially | |||
* Lateral rectus: abduction of eyeball | |||
* Medial rectus: adduction of eyeball | |||
Innervation: | |||
* All except lateral rectus: oculomotor n. (CN 3) | |||
* Lateral rectus: abducent nerve (CN 6) | |||
'''<u>Superior oblique</u>''': medial to the levator palpebrae superioris | |||
* <u>Origin</u>: body of the sphenoid bone. | |||
* <u>Insertion</u>: tendon pass through trochlea insert in sclera (deep to superior rectus). | |||
* <u>Function</u>: abducts, depresses and rotates eyeball medially. | |||
* <u>Innervation</u>: trochlear nerve (CN 4). | |||
'''<u>Inferior oblique</u>''' | |||
* <u>Origin</u>: anterior floor of the orbit (maxilla). | |||
* <u>Insertion</u>: Runs posterolaterally crossing the inferior rectus insert in sclera (deep to lateral rectus) | |||
* <u>Function</u>: abducts, elevates and rotated eyeball laterally | |||
* <u>Innervation</u>: oculomotor nerve (CN 3) | |||
[[Category:Anatomy]] | [[Category:Anatomy]] | ||
[[Category:Ophthalmology]] | [[Category:Ophthalmology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:13, 6 May 2024
There are 7 extra-ocular muscles - 6 of each responsible for moving the eye ball and 1 is responsible for raising the eyelids.
The extra-ocular muscles are:
Levator palpebrae Superioris (most superior extra-ocular muscle)
- Origin: lesser wing of sphenoid bone (superior-anterior to optic canal)
- Insertion: superior tarsus of the eyelid
- Function: raising the eyelid
- Innervation: superior division of the oculomotor nerve (CN 3).
- Unique feature: some of its inferior fibers are smooth muscle fibers - help with eyelid elevation. Innervated by post-ganglionic sympathetic fibers.
Rectus Muscles (superior, medial and lateral)
Origin: the common tendinous ring (all of the muscles)
Insertion: sclera (posterior to corneoscleral junction)
Function: the axis of the orbit and the axis of the eyeball aren’t the same
- Superior rectus: moves the eyeball superiorly and medially.
- Inferior rectus: moves the eyeball inferiorly and medially
- Lateral rectus: abduction of eyeball
- Medial rectus: adduction of eyeball
Innervation:
- All except lateral rectus: oculomotor n. (CN 3)
- Lateral rectus: abducent nerve (CN 6)
Superior oblique: medial to the levator palpebrae superioris
- Origin: body of the sphenoid bone.
- Insertion: tendon pass through trochlea insert in sclera (deep to superior rectus).
- Function: abducts, depresses and rotates eyeball medially.
- Innervation: trochlear nerve (CN 4).
Inferior oblique
- Origin: anterior floor of the orbit (maxilla).
- Insertion: Runs posterolaterally crossing the inferior rectus insert in sclera (deep to lateral rectus)
- Function: abducts, elevates and rotated eyeball laterally
- Innervation: oculomotor nerve (CN 3)