Peritoneum: Difference between revisions
| Line 90: | Line 90: | ||
===Reference=== | ===Reference=== | ||
[[Category:Anatomy]] | [[Category:Anatomy]] | ||
Revision as of 17:56, 22 June 2023
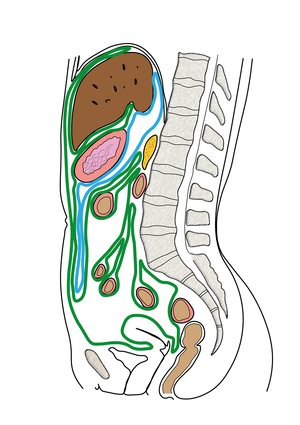
Peritoneum or peritoneum is a shiny serous membrane, covered by a single-layered epithelium mesothelium, which lines the abdominal cavity.[1] Under the peritoneum there is a subserosa, which fixes the peritoneum to the substrate.
On the anterior abdominal wall posteriorly in the tela subserosa, 3 ligamentous bands run from the bladder to the umbilicus, which are the remnants of the urachus and umbilical arteries. They form 3 plexuses : plica umbilicalis mediana, medialis dx. et sin.
They divide into:
a) peritoneum parietale - in the form of duplicates, necks, ligaments passes to the organs in the abdominal cavity
b) peritoneum viscerale - the peritoneum
The cavity between the two peritoneums cavitas peritonealis is filled with a small amount of fluid liquor peritonei.
According to their relationship to the peritoneum, organs are divided into : intraperitoneal, retroperitoneal, subperitoneal, extraperitoneal and secondary retroperitoneal
Hernia :
a)priama - anulus inguinalis superficialis, fossa inguinalis medialis
b) nepriama - anulus inguinalis profundus potom cez canalis inguinalis až do anulus inguinalis superfic., fossa inguinalis lateralis
Breakdown of the peritoneal cavity
- pars supramesocolica (nad mesocolon transversum, mezi ním a bránicí):
- spatium subphrenicum dx. et sin. (mezi bránicí a játry);
- spatium subhepaticum dx. et sin.;
- bursa omentalis (komunikuje s pravým subhepatickým prostorem prostřednictvím for. epiploicum).
Hranice bursa omentalis : ventrálne-žalúdok, omentum minus a lig. gastrocolicum, dorzálne - parietálne peritoneum, pankreas, veľké cievy, ľavá oblička a nadoblička, kaudálne mesocolon transversum
2. pars inframesocolica
Priebeh radix mesenterii a zrastenia colon ascendens a colon descendens a aj mesocolon transversum vytvárajú 4 priestory:
- pravé zrastové pole - kraniálne je mesocolon, vpravo colon ascendens a kaudálne radix
- ľavé zrastové pole - kraniálne mesocolon, vpravo radix mesenterii, vľavo colon descendens
- right and left paracolic space - lateral side of colon descendens/ascendens
Organ Ligaments
- v pars supramesocolica:
- coming from the mesogastrium dorsale:
- lig. phrenicolienale;
- lig. gastrophrenicum;
- lig. gastrolienale;
- lig. gastrocolicum;
- omentum majus - from curvatura gastrica major, has 2 leaves , the anterior one descends caudally in front of the transverse part of the colon, the posterior leaf returns upwards and attaches to the taeniae omentales of the colon
- arising from the mesogastrium ventrale:
- omentum minus (lig. hepatooesophagicum, lig. hepatogastricum et hepatoduodenale); - duplication between the curvature gastrica minor and the visceral surface of the liver
- lig. falciforme hepatis (in its continuation - lig. coronarium dx. et sin. et lig. triangulare dx. et sin.).
- coming from the mesogastrium dorsale:
- v pars inframesocolica:
- mesenterium;
- mesoappendix;
- mesocolon transversum - colon transversum
- variably mesocolon ascendens, descendens, sigmoideum and mesorectum.
Peritoneal recessions
Peritoneal recessions are blind pockets in the peritoneal cavity. They are sites of possible internal henia formation.
- in the duodenojejunal flexure area:
- rec. duodenalis sup. et inf. Treitzi;
- rec. retroduodenalis Waldayeri;
- rec. paraduodenalis (sinister, venosus - runs here v. mesenterica inf.) Gruberi-Landzerti.
- in the area of the ileocecal transition:
- rec. ileocaecalis sup. et inf.;
- rec. retrocaecalis;
- recessus paracolici;
- recessus intersigmoideus Treitzi.
Vascular supply
blood vessels of those organs which are surrounded by it
Nerve supply
Autonomic vasomotor nerves, the visceral is supplied autonomically and the parietal sensory innervates the n.phrenicus, nn. intercostales and plexus lumbalis
Links=
External links
Source
Reference
- ↑ {{#switch: book |book = Incomplete publication citation. ČIHÁK,. Anatomy. Prague : Grada Publishing, 2002. 2. Anatomy; 978-80-7262-438-6. |collection = Incomplete citation of contribution in proceedings. ČIHÁK,. Anatomy. Prague : Grada Publishing, 2002. 2. Anatomy; {{ #if: 80-247-0143-X |978-80-7262-438-6} } |article = Incomplete article citation. ČIHÁK,. 2002, year 2002, |web = Incomplete site citation. ČIHÁK,. Grada Publishing, ©2002. |cd = Incomplete carrier citation. ČIHÁK,. Grada Publishing, ©2002. |db = Incomplete database citation. Grada Publishing, ©2002. |corporate_literature = ČIHÁK,. Anatomy. Prague : Grada Publishing, 2002. 2. Anatomy; 978-80-7262-438-6} }