Angelman Syndrome
From WikiLectures
(Redirected from Angelman syndrome)
| English: Angelman syndrome |
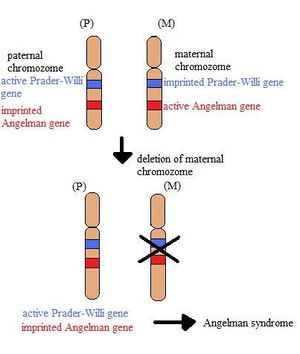
- This syndrome is caused by the loss of function of gene UBE3A - physiologically, just the maternal copy of this gene is functional (the paternal copy is imprinted, i.e. epigenetically silenced). Thus loss of the maternal gene causes this syndrome. The critical genomic region of this disorder is located on chromosome 15 (The Prader-Willi/Angelman Critical Region- PWACR; 15q11-q13). This genetic disorder is connected especially with the nervous system. Children are affected in their early age.
- Typical symptoms: severe intellectual disability and developmental delay, speech problems, ataxia, epilepsy or microcephaly.
- Patients are sometimes called "happy puppets" because of their behavior. They smile frequently, laugh and have flapping movements.
- Incidence of Angelman syndrome is 1 in 12 000 - 20 000 people worldwide.
Links[edit | edit source]
Related articles[edit | edit source]
Sources[edit | edit source]
Bibliography[edit | edit source]
- KUMAR, ABBAS, FAUSTO, MITCHELL,. Robbins Basic Pathology. 8th edition edition. 2007. ISBN 978-0-8089-2366-4.