Skin tumors: Difference between revisions
(originates from wikiskripta, skin tumors - https://www.wikiskripta.eu/index.php?title=N%C3%A1dory_k%C5%AF%C5%BEe&action=edit) Tag: Manual revert |
(original from wikiskripta, skin tumors - https://www.wikiskripta.eu/index.php?title=N%C3%A1dory_k%C5%AF%C5%BEe&action=edit) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== | == Basal cell carcinoma == | ||
{{Edituj článek|Bazaliom}} | {{Edituj článek|Bazaliom}} | ||
{{:Bazaliom}} | {{:Bazaliom}} | ||
== | == Spinal tumor == | ||
{{Edituj článek|Spinaliom}} | {{Edituj článek|Spinaliom}} | ||
{{:Spinaliom}} | {{:Spinaliom}} | ||
== | == Melanoma == | ||
{{Edituj článek|Melanom}} | {{Edituj článek|Melanom}} | ||
{{:Melanom}} | {{:Melanom}} | ||
== | == Kaposi's sarcoma == | ||
{{Edituj článek|Kaposiho sarkom}} | {{Edituj článek|Kaposiho sarkom}} | ||
{{:Kaposiho sarkom}} | {{:Kaposiho sarkom}} | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
{{:Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans}} | {{:Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans}} | ||
== | == Verrucous carcinoma == | ||
{{Edituj článek|Verukózní karcinom}} | {{Edituj článek|Verukózní karcinom}} | ||
{{:Verukózní karcinom}} | {{:Verukózní karcinom}} | ||
<noinclude> | <noinclude> | ||
== | == Links == | ||
=== Reference === | === Reference === | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
=== | === related articles === | ||
* [[Prekancerózy v dermatologii]] | * [[Prekancerózy v dermatologii]] | ||
* [[Benigní kožní nádory]] | * [[Benigní kožní nádory]] | ||
=== | === External links === | ||
* [[wikipedia:cs:Melanom|Melanom (česká wikipedie)]] | * [[wikipedia:cs:Melanom|Melanom (česká wikipedie)]] | ||
* [[wikipedia:en:Melanoma|Melanoma (anglická wikipedie)]] | * [[wikipedia:en:Melanoma|Melanoma (anglická wikipedie)]] | ||
=== | === References === | ||
* {{Citace | * {{Citace | ||
| typ = web | | typ = web | ||
Revision as of 15:37, 12 November 2022
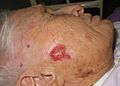
Basal cell carcinoma
__
It is the most common malignant skin tumor. Its incidence has doubled in the last 15 years.
Occurrence
We observe an increased incidence after the 1940s. years of age, the most risky is the group over 60. However, it can be at any age.
It affects almost exclusively white individuals, and when it occurs in pigmented races, it is associated with unusual etiological factors.
The tumor arises from keratinocytes epidermis.
Clinical picture, development
Typical cells are oval in shape and resemble the cells of the basal layer epidermis – hence the name.
The tumor almost never metastasizes - over 200 cases of metastases have been described worldwide, mostly to lymph nodes.
It usually starts as a nodule, boil or scab that does not change significantly at first.
It grows slowly, as if crawling on the surface.
It consists of a single solitary nodule with raised edges, parts may be subject to ulceration that does not heal.
Sometimes there is a false improvement, the ulcer almost heals, only to reappear before long and slowly enlarge.
An inconspicuous course often results in the formation eventually increasing to dimensions that can be a treatment problem in some locations.
On the other hand, basal cell carcinoma on the mucous membranes metastasizes very often.
Cause of disease
As with other malignant diseases, the cause of the disease is unclear.
The main etiological factor is chronic, long-term exposure of the skin to UV radiation.
Prognosis
With the exception of extensive or invasively growing tumors, basal cell carcinoma does not pose a threat to the patient's life. However, if the tumor grows long enough, it can form extensive foci with destruction of neighboring tissues.
Treatment
Surgical removal. If it is not cut out completely, it recurs! Excision is then necessary until the entire bearing is removed. Due to the place of occurrence (face), the aesthetic side of the procedure cannot be neglected.
Spinal tumor
__ Spinaliom
Melanoma
__ Melanom
Kaposi's sarcoma
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans
__
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is a malignant fibrous tumor, characterized by local invasion and frequent recurrence. The tendency to metastasize is small.
Clinical picture
It occurs as a rigid bearing on the upper body. During development, they form as painful brownish-red or bluish bumps with vascular ectasia on the surface. The tendency for infiltrations of the lower layers of the skin is relatively common. It metastasizes exceptionally to regional nodes or lungs.
Diagnosis
Histopathologically, it contains CD34 + fibroblasts in a typical storiform arrangement.
Differential diagnosis
Therapy
Surgical removal with a wide margin of at least 3-5 cm into healthy tissue and to a depth of fascia.
Prognosis
Chronic course, frequent recurrences after surgical treatment. Metastasizes rarely.
Verrucous carcinoma
Links
Reference