Leydig Cells: Difference between revisions
From WikiLectures
Petr Svetr (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Petr Svetr (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
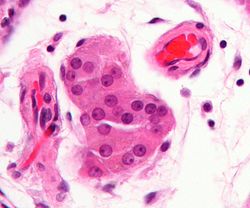
'''Leydig cells''' are rounded (polygonal) cells of the '''testicular interstitium''' with a centrally located nucleus and eosinophilic [[cytoplasm]]. Their main function is the production of male sex hormones, mainly [[Testosterone|'''testosterone''']] . Their function is influenced by the [[luteinizing hormone]] of the anterior lobe of the [[pituitary gland]]. | '''Leydig cells''' are rounded (polygonal) cells of the '''testicular interstitium''' with a centrally located nucleus and eosinophilic [[cytoplasm]]. Their main function is the production of male sex hormones, mainly [[Testosterone|'''testosterone''']] . Their function is influenced by the [[luteinizing hormone]] of the anterior lobe of the [[pituitary gland]]. | ||
Leydig cells can also rarely appear in women as part of the so-called ovarian Sertolli-Leydig tumor. <ref>{{Cite| type = web| surname1 = Gershenson| name1 = David M| url = https://www.uptodate.com/contents/sex-cord-stromal-tumors-of-the-ovary-tumors-with-granulosa-and-sertoli-leydig-elements?search=sex%20cord-stromal%20tumours&source=search_result&selectedTitle=2~150&usage_type=default&display_rank=2| | Leydig cells can also rarely appear in women as part of the so-called ovarian Sertolli-Leydig tumor. <ref>{{Cite| type = web| surname1 = Gershenson| name1 = David M| colective = yes| url = https://www.uptodate.com/contents/sex-cord-stromal-tumors-of-the-ovary-tumors-with-granulosa-and-sertoli-leydig-elements?search=sex%20cord-stromal%20tumours&source=search_result&selectedTitle=2~150&usage_type=default&display_rank=2| source_name = Sex cord-stromal tumors of the ovary: Sertoli-stromal cell tumors| date_of_revision = 2018-09-13| cited = 2023-01-20}}</ref><noinclude> | ||
== Links == | == Links == | ||
Revision as of 17:07, 20 January 2023
This article has been translated from WikiSkripta; ready for the editor's review.
Leydig cells are rounded (polygonal) cells of the testicular interstitium with a centrally located nucleus and eosinophilic cytoplasm. Their main function is the production of male sex hormones, mainly testosterone . Their function is influenced by the luteinizing hormone of the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland.
Leydig cells can also rarely appear in women as part of the so-called ovarian Sertolli-Leydig tumor. [1]
Links
Related articles
Sources
- VOKURKA, Martin – HUGO, Jan. Velký lékařský slovník. 9. edition. Maxdorf, 2009. pp. 1159. ISBN 978-80-7345-202-5.
- JUNQUIERA, L. Carlos – CARNEIRO, José – KELLEY, Robert O. Základy histologie. 1. edition. H & H, 1997. pp. 502. ISBN 80-85787-37-7.
- ↑ GERSHENSON, David M. Sex cord-stromal tumors of the ovary: Sertoli-stromal cell tumors [online]. The last revision 2018-09-13, [cit. 2023-01-20]. <https://www.uptodate.com/contents/sex-cord-stromal-tumors-of-the-ovary-tumors-with-granulosa-and-sertoli-leydig-elements?search=sex%20cord-stromal%20tumours&source=search_result&selectedTitle=2~150&usage_type=default&display_rank=2>.