Nutrient chemistry
Content of the subsection
- Nutrient overview – sacharides
- Nutrient overview – lipids
- Nutrient overview – proteins
Nutrient overview - sacharides
Clasification and structure
Sacharides, also called carbohydrates or glycids, are the most abundant organic substances on Earth. Their molecules are made up of oxygen, carbon and hydrogen atoms. From a chemical point of view, these are polyhydroxyaldehydes and polyhydroxyketones. They contain functional aldehyde or keto groups in their molecule, as well as a larger number of hydroxyl groups.
Clasification of carbohydrates
According to the number of units in the molecule, we distinguish:
- monosaccharides – cannot be further hydrolyzed into simpler units;
- oligosaccharides – they form 2–10 units of monosaccharides by hydrolysis;
- polysaccharides – hydrolyzing into more than 10 monosaccharides.
- Monosaccharides and oligosaccharides are generally called sugars. A synonym for polysaccharide is the word glycan.
We divide monosaccharides according to:
- Number of C-atoms: trioses, tetroses, pentoses, hexoses.
- Functional groups: aldoses and ketoses.
We divide polysaccharides into:
- Homopolysaccharides: these are polymers made up of the same type of monosaccharide. Examples are starch, glycogen or cellulose.
- Heteropolysaccharides: they are polymers made up of more than one type of monosaccharide. An example is hemicellulose.
Strukturu molekuly sacharidu můžeme vyjádřit různými vzorci:
- Lineární (Fischerův) vzorec;
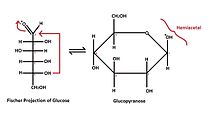
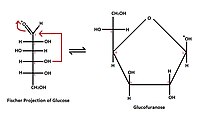
- Cyklický (Hawortův) vzorec, který vzniká vytvořením heterocyklické struktury.
- Cyklus může být:
- šestičlenný – pyranóza – podle podobnosti se šestiuhlíkatým pyranem;
- pětičlenný – furanóza – podle podobnosti s pětiuhlíkatým furanem.
- Tollensův vzorec popisuje tvorbu cyklické struktury ze vzorce lineárního. Ukazuje reakci hydroxylu s karbonylovou skupinou za vzniku tzv. poloacetalové (hemiacetalové) struktury.
Izomerie
Je to stav, kdy mají sloučeniny se stejným sumárním vzorcem jiné strukturní uspořádání atomů v molekule. U molekul sacharidů se setkáváme s následujícími druhy izomerie.
- Template:D- a Template:L- řada
- Označuje se podle pozice −OH skupiny na posledním chirálním uhlíku. Přiřazení k příslušné řadě vychází z podobnosti s výchozí sloučeninou sacharidové řady – glyceraldehydem. Skupina −OH se ve Fischerově vzorci nachází vpravo pro Template:D- a vlevo pro Template:L- izomery.
- Template:D- a Template:L- izomery jsou zrcadlovými obrazy tzv. enantiomery – optické izomery. Liší se znaménkem optické otáčivosti, neboli směru, ve kterém otáčejí rovinu polarizovaného světla.
- Neplatí však obecně, že by Template:D- řada byla pravotočivá a Template:L- řada levotočivá.
- Ekvimolární směs enantiomerů se nazývá racemická směs, nebo také Template:DTemplate:L směs, a optickou aktivitu nevykazuje.
- V přírodě se vyskytují častěji Template:D- izomery .
- Pyranózy a furanózy
- Označují se podle podobnosti cyklické formy příslušného monosacharidu s cyklem pyranu nebo furanu. Glukóza v roztoku se vyskytuje z více než 99 % ve formě gluko-pyranózy, zbylá část molekul, méně než 1 %, se pak objevuje ve formě gluko-furanózy.
- α- a β- anomery
- Označují se podle polohy hemiacetálového nebo hemiketalového −OH v cyklu. Hemiacetaly vznikají reakcí aldehydové a alkoholové skupiny, hemiketaly reakcí keto- a alkoholové skupiny.
- Pokud je −OH skupina orientována na stejnou stranu jako −OH skupina označující příslušnost k Template:D- nebo Template:L- řadě, jde o α-anomer. Pokud je −OH skupina orientována na stranu protilehlou, jedná se o β-anomer.
Anomery se liší optickou otáčivostí. First definition of ecotoxicology (1969): René Truhaut: the study of the adverse effects of chemicals with the aim of protecting natural species and communities. Rachel Carson (1962): the memoir The Silent Spring highlights the use of pesticides , especially DDT and other agrochemicals. The book led to the establishment of the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the USA. Introduction of methods describing the toxic effects of human-produced substances on the environment and the organisms contained therein. Systematic implementation of fish toxicity testing methods. In addition to direct toxic effects, the effects of bioconcentration and bioaccumulation are studied – increases in the concentration of foreign substances in the tissues of organisms as a result of exposure from the environment.
2004 EC ratification: Persistent Organic Pollutants Protocol to the 1979 Convention on Long-Range Transboundary Air Pollution The aim of the protocol is to limit, reduce or eliminate the discharge, emissions and losses of persistent organic pollutants that have significant adverse effects on human health or the environment due to long-range transboundary air transport.
In 2006 , Regulation No. 166/2006 of the European Parliament and the EC Council was issued, establishing the European Register of Releases and Transfers of Pollutants . It represents a publicly accessible database of pollutant releases into the air, water and soil, information on wastewater, information on pollutant releases from dispersed sources.
In 2003 , the proposal for a new framework for legislation covering the safety of chemicals REACH (Registration, Evaluation and Authorization of Chemicals) was accepted by the European Commission and approved by the European Parliament . Enterprises and firms that import more than 1 ton of a chemical compound per year will be forced to register this chemical in a central data bank. The aim is to improve the protection of the health of nature, including people, to increase the innovation capacity and the ability of the chemical industry to compete in the European Union. The new measures concern not only new chemical substances introduced to the market, but also substances that have been used for a long time. The program aims to ensure that by 2020 at the latest, only chemical substances with known properties and in a way that does not harm human health and the environment are used.
- Epimery
- Liší se od sebe polohou jedné −OH skupiny v molekule.
Příkladem jsou glukóza a manóza.
- Aldózy a ketózy
- Označují se podle odlišné funkční skupiny na 1. a 2. uhlíku molekuly.