Angiotensin
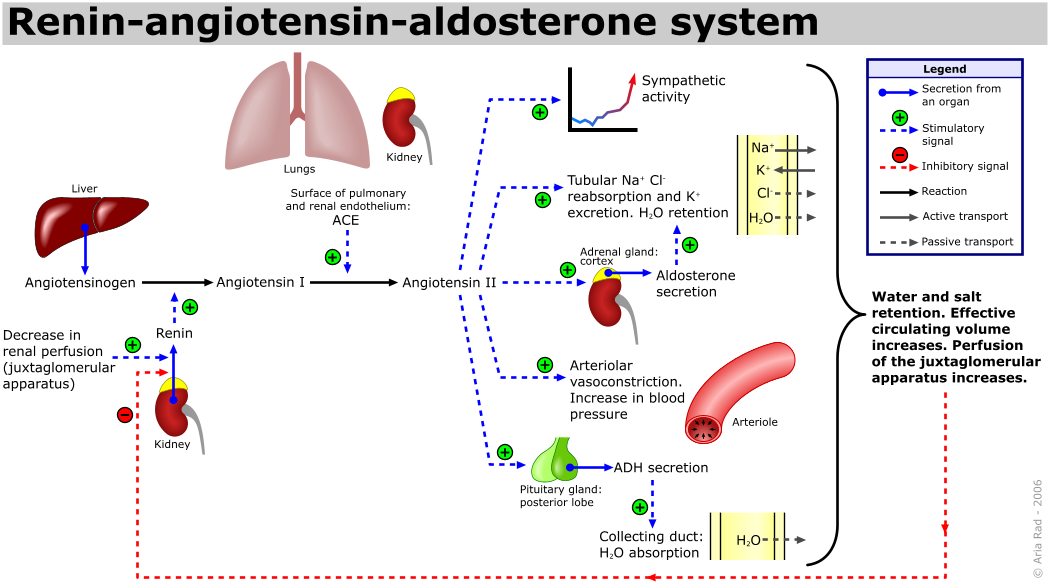
Angiotensin is an oligopeptide playing a major role in blood pressure regulation . It is part of the so-called renin-angiotensin system. This system represents the stepwise conversion of the angiotensin precursor, angiotensinogen, to the final product of this system, angiotensin II.
Angiotensinogen is a plasma protein (α 2 -globulin) which is a precursor for the first of the intermediate products of the renin-angiotensin system, angiotensin I. It is produced due to the action of the enzyme of the juxtaglomerular apparatus of the kidneys, renin . Renin cleaves several amino acids (3) from angiotensinogen to form angiotensin I.
Angiotensin I is chemically a decapeptide, which is further converted in the blood, especially in the lungs, by angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) to angiotensin II.
Angiotensin II is an active component of the renin-angiotensin system. It has a very strong vasoconstrictive effect on resistance vessels, especially on arterioles, activates the sympathetic system and stimulates the secretion of aldosterone.
Amino acid order:[edit | edit source]
- Angiotensinogen
- Angiotensin I
- Angiotensin II
Sources[edit | edit source]
Related Articles[edit | edit source]
External Links[edit | edit source]
Použitá literatura[edit | edit source]
- KITTNAR, Otomar. Lékařská fyziologie. 1. edition. Grada, 2011. 790 pp. ISBN 978-80-247-3068-4.
Recommended Literature[edit | edit source]
- TROJAN, Stanislav – TROJAN, Stanislav. Lékařská fyziologie. 4. edition. Grada, 2003. 772 pp. ISBN 80-247-0512-5.
- SILBERNAGL, Stefan – DESPOPOULOS, Agamemnon. Atlas fyziologie člověka. 6. edition. Grada, 0000. 0 pp. ISBN 80-247-0630-X.