Antebrachial region
Region of the upper limb between elbow and the wrist. The bones of the forearm are the radius (lateral side) and the ulna (medial side). Muscles of the forearm form three compartments separated by fascia, anterior, posterior and lateral. Muscles of the anterior compartment are innervated mainly by the median nerve with the exceptions of Flexor carpi Ulnaris and flexor digitorum profundus. Flexor carpi ulnaris is innervated by ulnar nerve and flexor digitorum profundus has dual innervation by both median and ulnar nerves. The posterior compartment muscles are innervated by the radial nerve. Blood supply is provided by the radial, ulnar and interosseous arteries. Meanwhile venous return is facilitated by the cephalic, basilic and deep veins which run along side arteries and carry the same names.
Muscles of the antebrachium[edit | edit source]
The Anterior compartment:
superficial layer
- Musculus pronator teres
- Musculus flexor carpi radialis
- Musculus palmaris longus
- Musculus flexor carpi ulnaris
second layer
- Musculus flexor digitorum superficialis
third layer
- Musculus flexor digitorum profundus
- Musculus flexor pollicis longus
fourth, deep layer
- Musculus pronator quadratus
Lateral compartment:
superficial layer
- Musculus brachioradialis
- Musculus extensor carpi radialis longus
- Musculus extensor carpi radialis brevis
deep layer
Musculus supinator
Posterior compartment:
superficial layer
- Musculus extensor digitorum
- Musculus extensor digiti minimi
- Musculus extensor carpi ulnaris
deep layer
- Musculus abductor pollicis longus
- Musculus extensor pollicis brevis
- Musculus extensor pollicis longus
- Musculus extensor indicis
Notable structures[edit | edit source]
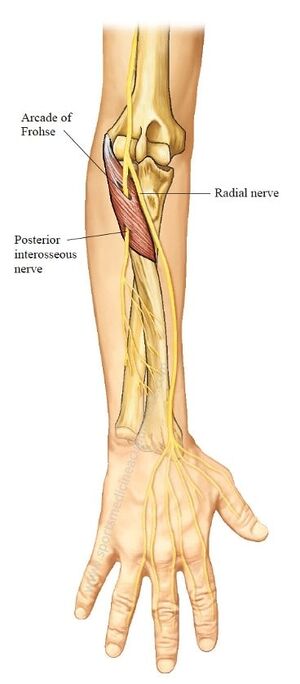
Supinator canal also known as arcade of Frohse is a canal for the posterior interosseus nerve( branch of the radial nerve) in the proximal part of the supinator, obstruction of which can cause symptoms similar to those of lateral epicondylitis.
Used literature[edit | edit source]
- ČIHÁK, Radomír a Miloš GRIM. Anatomie 1. 3. vydání. Praha : Grada, 2011. 534 s. ISBN 978-80-247-3817-8.
- PETROVICKÝ, Pavel, et al. Anatomie- pohybový aparát končetin. 1. vydání vydání. Praha : Karolinum, 1995. s. 432. ISBN 80-7184-108-0.