Atlanto-occipital dislocation
From WikiLectures
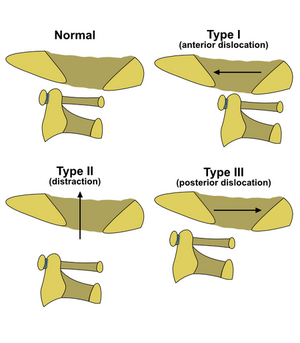
Atlantooccipital dislocation (AOD) is a result of an injury to the ligamentous complex connecting the atlas bone and the occipital bone of the head.
According to the clinical picture, we divide patients into 2 groups:
- Without a significant neurological lesion (CAVE: overlooked injury),
- With a severe deficit and impaired vital functions.
The graphic examination consists of:[edit | edit source]
- X-ray of the craniocervical junction in the transoral projection and the lateral projection (standard anteroposterior CC does not show the transition due to summation with the lower jaw), * CT, or MRI.
Therapy: A fundamental contraindication is a traction in the longitudinal direction!
- The surgical solution includes occipitocervical fusion through a posterior approach and then 3 months of fixation in a Philadelphia collar (general rule after a surgical solution of cervical spine injuries),
- A conservative option is several months of immobilization in a light vest.
Links[edit | edit source]
External links[edit | edit source]
- Mefanet: http://mefanet.lfp.cuni.cz/clanky.php?aid=328, Poranění páteře
- PubMed: Atlanto-occipital dislocation
References[edit | edit source]
- SAMEŠ, M, et al. Neurochirurgie. 1. edition. Praha : Jessenius Maxdorf, 2005. ISBN 80-7345-072-0.