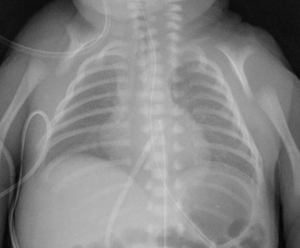
Cleidocranial dysplasia
Cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD) is a very rare autosomal dominantly inherited disease that affects the development of bones, skull and teeth. A typical sign is partial or full aplasia of the clavicles, tooth anomalies, delayed closing of the fontanelles, as well as osteopenia , hearing disorders, hand bone abnormalities, recurrent otitis and sinusitis. People with CCD may develop scoliosis, osteoporosis, and short stature.
The disorder is most often caused by the presence of mutations in the RUNX2 gene (Runt-related transcription factor 2), whose protein product is a key transcription factor affecting osteoblast differentiation and bone morphogenesis.
There is no causal treatment, the care is aimed at alleviating difficulties and depending on the severity of the symptoms, a craniofacial surgeon, dentist, orthodontist, endocrinologist, otorhinolaryngologist, speech therapist and orthopedist are involved.
Links[edit | edit source]
Related Articles[edit | edit source]
External links[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center. Cleidocranial dysplasia [online] [online]. The last revision 19-08-2020, [cit. 16-03-2023]. <https://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/6118/cleidocranial-dysplasia>.
National Organization for Rare Disorders. Cleidocranial Dysplasia [online] [online]. [cit. 16-03-2023]. <https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/cleidocranial-dysplasia/>.