Defects of optical systems
Defects optical systems (optical aberrations) are deviations of the display of a real optical system from the display of an ideal optical system. As a result, the point does not appear as a point, but as a "flat" with an uneven distribution of intensity, which leads to a deterioration of the image quality (reduction of contrast, blurring of the image, color change, geometric distortion of the image, ...)
Distribution of aberrations[edit | edit source]
Analytically[edit | edit source]
- Geometric Defects
- Monochromatic
- Axial defects
- Hole defect
- Off-axis defects
- Coma
- Astigmatism
- Arching the field
- Distortion
- Axial defects
- Chromatic
- Image size
- Size color defect
- Image position
- Position color defect
- Image size
- Monochromatic
- Wave Aberration
Synthetically[edit | edit source]
- Discernment
- Edge sharpness
- Contrast transfer function
Geometric defects[edit | edit source]
Hole Defect[edit | edit source]
Aperture (spherical) defect (spherical aberration) arises when the axis point is imaged with a wide beam.
The image of the point is a circular area (image blur).
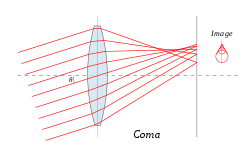
Coma[edit | edit source]
Coma is an optical defect, when a wide beam of rays emanating from a point that lies behind the optical axis forms complicated figures resembling comets after passing through the optical system. This beam is not parallel to the optical axis. The degree of image distortion increases with increasing distance of the light source from the axis of the optical system.
This malfunction can be caused by an inaccurate design of the optical system.
Astigmatism[edit | edit source]
A defect in the optical system where rays of lights incident in two perpendicular planes to the optical axis are projected at two different distances. It is caused by irregular curvature of the lens. This aberration creates a blurred and distorted image. Astigmatism occurs especially when viewing objects that are viewed at a large angle of view, for example when photography.
Astigmatic difference - is a term that expresses the distance between the points on the optical axis where rays from mutually perpendicular planes (axes) intersect.
Focal points - mean the line segments between these points on the optical axis.
Anastigmat - a system of lenses that compensates for astigmatism.
Arching field[edit | edit source]
Field of view curvature is an aberration where points of a plane perpendicular to the optical axis are displayed on a curved surface. They should be correctly projected in a plane perpendicular to the optical axis. It follows that the image will be curved and sharp in different places. This defect is related to astigmatism.
Distortion[edit | edit source]
A defect in which the magnification of the peripheral points of an object is different from the magnification of the points located in the center of the object. We recognize two types of distortion:
- barrel distortion – the outer points of the object are magnified more than the inner points
- pincushion distortion – the outer points of the object are magnified less than the inner points
Color flaw[edit | edit source]
 A color defect (chromatic aberration) is manifested when the object is displayed with polychromatic radiation' (white light).
A color defect (chromatic aberration) is manifested when the object is displayed with polychromatic radiation' (white light).
The focal length of a lens depends on the refractive index and this varies according to the color of the light used (that is, according to the wavelength). Any ray of white light after passing through the optical system corresponds to the entire spectrum of rays corresponding to individual wavelengths. When passing through a lens with a color defect, light decomposition occurs.
They are caused by the dispersion of optical materials.
As a result of a color defect, the image of a point is a point of a certain color, which is surrounded by rings of other colors (iridescent coloring of the edges, blurring of the image). Chromatic defect can be partially removed by achromatizing the optical system (using a suitable combination of connective and dispersive lenses)
Color defect size[edit | edit source]
It manifests itself when displaying the object's off-axis points. The size of the image depends on the wavelength of lights. The created image of the object is lined with color.
Position color defect[edit | edit source]
For a given beam, a whole spectrum of images corresponding to individual wavelengths is created in the object space. The image is out of focus.
Wave Aberrations[edit | edit source]
Wave aberration is given by the optical path between the wavefront associated with the real rays and the spherical (spherical) wavefront that would correspond to an ideal display. Using wave aberrations, a diagnostic method, the so-called wavefront analysis, was developed. The most modern refractive lasers are built on its basis.
Links[edit | edit source]
Related Pages[edit | edit source]
External links[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
- NOVAK, J.. Geometric Optics [online]. [cit. 2013-12-2]. <http://webfyzika.fsv.cvut.cz/PDF/prednasky/aberace_opt_soustav.pdf>.
- FALHAR, M.. Optical defects [online]. [cit. 2013-12-2]. <http://www.optikarium.cz/brylove-cocky-a-bryle/opticke-vady-uvod-1-cast>.
- UNKNOWN,. Display defects (aberrations) [online]. [cit. 2013-12-2]. <https://physics.mff.cuni.cz/kfpp/skripta/kurz_fyzyky_pro_DS/display.php/optika/3_3>.
References[edit | edit source]
- NAVRÁTIL, Leoš – ROSINA, Joseph, et al. Medical Biophysics. 1 (reprint 2013) edition. Grada Publishing, 2005. 524 pp. ISBN 978-80-247-1152-2.
- LEPIL, Oldrich – ŠEDIVÝ, Přemysl. Physics for grammar schools. Electricity and magnetism. 6. edition. Prometheus, 2012. ISBN 978-80-7196-385-1.
- TOMSA, J.: Optics (presentation)