Diagnostic imaging methods during chest examination
Anatomy[edit | edit source]
X-ray of chest[edit | edit source]
A chest X-ray is a basic examination method with minimal radiation exposure (0.01−0.02 mSv).
A summation chest image is taken:
- standing in PA projection (back-to-front image) ,
- supine in AP projection (anteroposterior image),
- lateral image — left or right (the pathology is closer to the plate),
- oblique image (I. and II. oblique),
- targeted images (imaging special pathology),
- image in lordotic projection (lingula),
- lung apex and upper thoracic aperture image.
The reporting value is highly dependent on the image quality:
- exposure,
- centering,
- the correct position of the patient (so that he is not curled up in the image and both lung wings are captured in their entirety),
- tilting,
- enough inspiration
- removal of jewelry (chain).
Chest X-ray evaluation[edit | edit source]
Evaluation of a chest image is difficult, requiring many years of practice (thousands of examinations). In short, we evaluate:
- bone structure,
- contours of the mediastinum , pulmonary hilae,
- contours of the cardiac shadow, calcification in the cardiac shadow,
- vessels — distribution of the vascular pattern, width of the truncus intermedius , signs of congestion in the small circulation,
- lung parenchyma – obscuration of an interstitial or alveolar character, focal shadows (tumor, metastasis, aspergilloma),
- lung development ( Pneumothorax , lobe collapse),
- pleural fluid — blunting of the costophrenic angles, veiling of the lung wing,
- position of foreign bodies ( central venous catheter , sternotomy suture , pacemaker , chest drain).
Radiological syndromes[edit | edit source]
- pleural effusion
- infiltrative shadowing with "air bronchogram" (indicative of pneumonia)
- diffuse increase in the transparency of lung fields (emphysema)
- atelectasis (lobar, alar)
- decay processes (TBC caverns, Jores cavern)
- disseminated pulmonary processes (diffuse reticulonodular drawing)
- bilateral hilar lymphadenomegaly (in sarcoidosis)
- pneumothorax, missing lung pattern lateral to the edge of the collapsed lung
- image of a "tinker bell" — cavity syndrome with a round dense mass inside (aspergilloma)
Predilection localization[edit | edit source]
- basally, laterally — interstitial pulmonary fibrosis
- pulmonary apex, upper lobes — TB
- hila, middle lung field — sarcoidosis
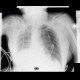
|
RTG hrudníku AP vleže: levostranný PNO |
| RTG hrudníku vstoje: pneumomediastinum |

|
RTG hrudníku: rozšíření horního mediastina a deviace trachey na podkladě strumy |
| RTG hrudníku: pleurální výpotek |
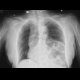
|
RTG hrudníku: brániční hernie |
Computed Tomography (CT)[edit | edit source]
CT hrudníku[edit | edit source]
Routine chest CT from the jugular to the external costophrenic angles with intravenous iodine contrast is the gold standard for the examination of the mediastinum and focal changes in the lung parenchyma.
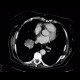
|
CT hrudníku: tumor plic |
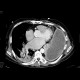
|
CT hrudníku: empyém hrudníku |
HRCT of lungs[edit | edit source]
Native CT of the chest with a reconstruction algorithm for enhancing the interface is the gold standard for diagnosing especially diffuse lung diseases such as interstitial lung processes , inflammatory changes in immunocompromised patients (e.g. pneumocystis pneumonia) and their follow-up.
| HRCT plic: idiopatická plicní fibróza |
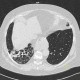
|
HRCT plic: bronchiektázie |
CT angiography of the lung[edit | edit source]
The examination is indicated for suspected acute pulmonary embolization , for pulmonary hypertension (to rule out the secondary etiology of pulmonary hypertension), to display vascular anomalies. It is necessary to ensure good venous access (flow rate at least 3 ml/s).

|
Angio-CT plicnice: sekundární (postembolická) plicní hypertense |

|
Angio-CT plicnice: akutní plicní embolie |
CT angiography of the thoracic aorta and aortic arch[edit | edit source]
Examination of the thoracic aorta is performed in the arterial phase (using the bolus-tracking method), it is most often indicated for suspected dissecting aneurysm , aortic rupture, and also as a control examination for monitoring aneurysms and postoperative conditions, to rule out stenosis or anomalies in the distance between the branches of the aortic arch.

|
Angio-CT hrudní aorty: disekující aneurysma hrudní aorty |
CT of the heart[edit | edit source]
A special examination method with ECG synchronization. Depending on when the data is captured, we distinguish:
- ECG gating — the x- ray is on all the time,
- ECG pulsing — reduction of X-ray machine power outside the specified interval.
What is needed is a CT machine with a higher time resolution (shorter rotation time or two x-rays). The examination is most often indicated for the evaluation of coronary artery stenosis and the patency of bypasses . It is not indicated in patients with clear symptoms of acute myocardial infarction (the patient is catheterized), the assessment of stenosis in patients with significant calcifications in the coronary artery wall is limited due to the "blooming" artifact. Another indication is left atrial CT before planned radiofrequency ablation .

|
CT srdce: koronární tepny na 16 řadém přístroji |
Hrubší patologie srdce a perikardu, jako např. tekutinu v perikardu, lze zobrazit i bez synchronizace s EKG.

|
CT hrudníku: perikardiální výpotek |
Magnetic Resonance (MR)[edit | edit source]
MR of the mediastinum[edit | edit source]
MR mediastinum can be indicated as an alternative to CT of the chest or to angio-CT of the large vessels of the mediastinum.
MR of the heart[edit | edit source]
MR heart is used to display structural changes of the myocardium (scar after a heart attack , myocarditis ), heart tumors, accurate measurement of the kinetics of individual compartments. In children, it is used to examine congenital heart defects.
Links[edit | edit source]
Související články[edit | edit source]
External links[edit | edit source]
- Images at atlas.mudr.org:
- Learning portal 1. LF UK - Radiodiagnostics: Quiz: imaging methods during chest examination
- http://www.lf3.cuni.cz/opencms/export/sites/www.lf3.cuni.cz/cs/pracoviste/3interni/vyuka/el_srdce_a_plice_dil1.pdf
- Heart and lungs (Modern textbook of cardiology and pneumology) - Petr Widimský et al. http://www.lf3.cuni.cz/opencms/export/sites/www.lf3.cuni.cz/cs/pracoviste/3interni/vyuka/el_srdce_a_plice_dil1.pdf


