Diagnostic imaging methods in retroperitoneum examination
Anatomy of Retroperitoneum[edit | edit source]
The retroperitoneum contains the following organs:
X-ray native abdominal image[edit | edit source]
A native image of the abdomen provides only very limited information about the organs of the retroperitoneum. In the field of retroperitoneum, we focus on:
- the contours of the psoas, which tend to be unilaterally obliterated in retroperitoneal bleeding and can be contoured by air strips in pneumoretroperitoneum,
- calcification in the wall of the aorta and iliac arteries' − if the arteries are significantly calcified, their expansion ( aneurysm ) can be visualized,
- contours of the kidneys - if they are not covered by summation with intestinal loops, more significant shape and size deviations can be discerned,
- contrast lithiasis' – shadows of calcification saturation in the course of the urinary tract,
- calcification in the pancreas.
| Nativní snímek břicha: pneumoretroperitoneum |
Ultrasound[edit | edit source]
Ultrasound is the basic examination method in the diagnosis of retroperitoneum disease. However, in many cases it is insufficient due to the position of the retroperitoneal organs - some may not be visualized at all.
Renal ultrasound[edit | edit source]
The kidneys can be visualized on ultrasound almost always and well. It is evaluated:
- kidney size - small kidneys in chronic nephropathy, large kidneys in pyelonephritis, acute renal insufficiency,
- kidney shape - irregular contours in chronic nephropathy and cortical scars,
- kidney position - dystopia, most often pelvic,
- congestion in the hollow system, possibly enlargement of the proximal part of the ureter,
- focal changes - cortical or parapelvic cysts, angiomyolipoma, carcinoma,
- vascular supply - renal artery stenosis (cannot always be evaluated), resistance index in the periphery
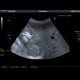
|
USG břicha: karcinom ledviny |
Adrenal ultrasound[edit | edit source]
In well-examined patients, expansions can be seen in the area of the adrenal glands, where adenomas are most often found. The right adrenal gland can be visualized better, examination of the adrenal gland is more difficult and less reliable.
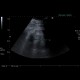
|
Abdomen USG: adrenal myelolipoma |
Pancreatic ultrasound[edit | edit source]
In most cases, the entire length of the pancreas cannot be visualized due to gas overlay in the digestive tract. It is evaluated:
- size - enlargement in acute pancreatitis, atrophy in chronic pancreatitis,
- enlargement of Wirsungi duct − chronic pancreatitis, tumor,
- boundary of the pancreas and possibly percolation of peripancreatic fat (in acute pancreatitis),
- echogenicity - limited reporting value (and especially clinical unusability) of the finding of a lipomatous pancreas (increased echogenicity),
- focal changes - pseudocysts, cysts, tumors, calcifications.
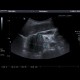
|
USG břicha: tumor hlavy pankreatu |
Ultrasound of the duodenum[edit | edit source]
In adult patients, the most common pathology is reactive inflammatory expansion of the wall during inflammation of the surrounding organs:
In newborns, ultrasound is used in the diagnosis of pylorostenosis.
Ultrasound of retroperitoneum vessels[edit | edit source]
- Aorta - ultrasound is used in the detection and monitoring of abdominal aortic aneurysm, as well as in the examination of renal arteries to rule out stenosis.
- Inferior vena cava' - visualization of thrombosis, caval filter position, respiratory flow variation.
- Portal vein - enlargement of the portal vein and its tributaries and slowing of flow in portal hypertension can be displayed, as well as occlusion (thrombosis) of the portal trunk or branches with possible by cavernous transformation and the development of a collateral riverbed.
Others[edit | edit source]
- Nodules - if the para-aortic area is not covered by gas in the intestinal loops, it is possible to visualize here enlarged lymph nodes.
Computed Tomography (CT)[edit | edit source]
Computed tomography is the most accurate imaging method for retroperitoneum pathologies.
CT abdomen and pelvis (routine)[edit | edit source]
The most common procedure - a regular CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis with intravenous application of iodine contrast agent and after oral preparation, usually 10 ml of iodine contrast agent in 500 ml of water.
| CT břicha: paraaortální lymfadenopatie |
Adrenal CT[edit | edit source]
Without oral preparation. A native examination is usually sufficient. When an expansion that does not have the natively unambiguous character of an adenoma or myelolipoma is detected, a post-contrast examination and a delayed phase are added, which distinguish the adenoma from other pathologies (hemorrhage, cyst, pheochromocytoma, lymphoma, metastasis, cancer) with a relatively high degree of certainty. When the adrenal gland enlarges without a visible focus, it is hyperplasia.

|
CT nadledvin: adenom |
CT kidney[edit | edit source]
The CT examination can be supplemented with an excretory phase to differentiate intrasinusoidal cysts from congestion, display anomalies of the calicopelvic system, delimitation of tumors of the excretory system or evidence of urinoma.
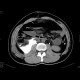
|
CT - vylučovací fáze: urinom |
CT angiography of the abdominal aorta and renal arteries[edit | edit source]
CT of the aorta is usually indicated for assessment of abdominal aortic aneurysm before its interventional or surgical solution, to monitor its size or stentgraft position. Assessment of the degree of renal artery stenosis is often adversely affected by artifacts (blooming) from calcified plaques in the wall.
CT portography[edit | edit source]
CT examination targeted at the portal tract (different delay and amount of blood flow) to rule out thrombosis, visualization of collateral circulation, occlusion by external compression or tumor infiltration.
| CT portografie: thrombosa porty |
CT in retroperitoneal bleeding[edit | edit source]
We perform a CT examination in two stages:
- as CT angiography and
- in the venous phase.
In addition to the hematoma itself, we will also show the leakage of opacified blood outside the vascular bed in the case of active bleeding.

|
CT angiografie: ruptura aneurysmatu abdominální aorty |
CT fistulography[edit | edit source]
CT examination of the abdomen without oral preparation, before the examination, the drain or fistula is injected with a diluted iodine contrast agent.
| CT fistulografie: enterokutánní píštěl po splenektomii |
Magnetická rezonance (MR)[edit | edit source]
- It has good sensitivity for characterizing adrenal expansions.
- It is an equivalent alternative to renal CT in imaging focal processes and staging renal carcinoma.
- Due to poorer spatial resolution, it is not suitable for searching for stones in the hollow system of the kidney.
- It is suitable for the characterization of focal expansions of the pancreat, MRCP will show the ductus Wirsungi well.
- It is an alternative to CT angiography when demonstrating stenosis of the renal arteries, in addition, significant atherosclerotic calcifications in the distance between the renal arteries are not an obstacle to the assessment of stenosis on MRI.

|
MR břicha: chronická píštěl po enukleaci tumoru pankreatu |
Links[edit | edit source]
Related articles[edit | edit source]
- Diagnostic imaging methods in the examination of the digestive tract
- Diagnostic imaging methods in the examination of the gallbladder and bile ducts
- Radiodiagnostic examination of the urinary tract
External links[edit | edit source]
- Images at atlas.mudr.org
- Learning portal 1. LF UK - Radiodiagnostics: Kvíz: zobrazovací metody při vyšetření retroperitonea
