ECG Leads
From WikiLectures
The 12 Conventional ECG Leads[edit | edit source]
These 12 leads are divided into two groups:
- six extremity (limb) leads; they are recording electrical potentials transmitted into the frontal plane;
- six chest (precordial) leads, they are recording electrical potential transmitted into horizontal plane.[1]
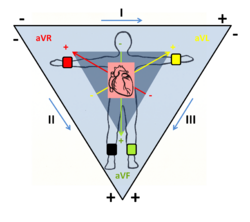
There are the leads with their location and polarity[2]:
| limb | location of the lead | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| bipolar extremity leads
-Einthoven's leads- | ||||||
| I | + | left upper limb | - | right upper limb | ||
| II | left lower limb | right upper limb | ||||
| III | left lower limb | left upper limb | ||||
| unipolar extremity leads
-Goldberg's leads- | ||||||
| aVR | right upper limb lead | |||||
| aVL | left upper limb lead | |||||
| aVF | left lower limb lead | |||||
| unipolar chest leads
-Wilson's leads- |
V1 | fourth intercostal space, just to the right of the sternum | ||||
| V2 | fourth intercostal space, just to the left of the sternum | |||||
| V3 | midway between V2 and V4, fifth intercostal space | |||||
| V4 | fifth intercostal space, midclavicular line on the left | |||||
| V5 | fifth intercostal space, anterior axillary line | |||||
| V6 | fifth intercostal space, midaxillary line | |||||
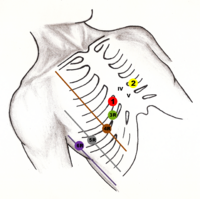
Additional ECG Leads[edit | edit source]
These leads are used in special situations, when conventional 12-leads ECG cannot reliably show the myocardial defect.[1]
Below are some examples of additional ECG leads[2]:
| lead | location of the lead | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| unipolar chest leads | V7 | posterior axillary line, on the same level as V6, on the left | ||||
| V8 | scapulary line, in the same level as V6, on the left | |||||
| V9 | paravertebral line on the left, on the same level as V6 | |||||
| VE | just to the left of processus xiphoideus | |||||
| V3R - V6R | on the right, same location as V3–V6 | |||||
| unipolar chest leads | V1´– V6´ | about 1 intercostal space above the V1–V6 | ||||
| V1´´– V6´´ | about 2 intercostal space above the V1–V6 | |||||
| esophageal leads | E/Oe | for example 37.5 cm (left atrium) | ||||
Links[edit | edit source]
Related articles[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Jump up to: a b KASPER, Dennis L – FAUCI, Anthony S – LONGO, Dan L, et al. Harrison's principles of Internal Medicine. 16th edition. New York : McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc, 2005. 2607 pp. pp. 1312-1313. ISBN 0-07-139140-1.
- ↑ Jump up to: a b WikiSkripta. Elektrokardiografie [online]. ©2011. The last revision 2011-07-2, [cit. 2011-07-03]. <http://www.wikiskripta.eu/index.php/Elektrokardiografie>.
Bibliography[edit | edit source]
- KASPER, Dennis L – FAUCI, Anthony S – LONGO, Dan L, et al. Harrison's principles of Internal Medicine. 16th edition. New York : McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc, 2005. 2607 pp. pp. 1311-1319. ISBN 0-07-139140-1.