Gallbladder and Extrahepatic Bile Ducts
From WikiLectures
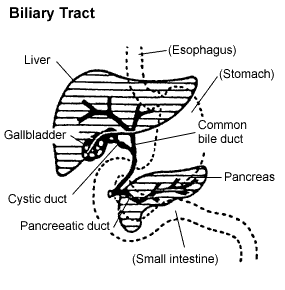
The gallbladder receives bile from the liver through the hepatic ducts for storage and later release, which aids in the digestion of fats.
Gallbladder[edit | edit source]
The gallbladder consists of the: fundus, body and neck:
- the fundus is on the inferior border of the liver,
- the body is on the transverse colon and superior part of duodenum,
- the neck has mucosal folds and drains into the cystic duct.
Anatomical Position[edit | edit source]
- Location: intraperitoneally, in the upper right abdomen, in the gallbladder fossa
- Projection: fundus projects onto the 9th rib
Bile Ducts[edit | edit source]
- The left and right hepatic ducts fuse to form the common hepatic duct.
- The common hepatic duct then fuses with the cystic duct to become the common bile duct.
- The common bile duct then joins with the pancreatic duct to form the Ampulla of Vater, which drains into the major duodenal papilla.
Links[edit | edit source]
Related Articles[edit | edit source]
Bibliography[edit | edit source]
- SNELL, Richard S. Clinical Anatomy by Regions. 8th Edition edition. 2004. ISBN 978-0-7817-6404-9.
- ↑ Sobotta Anatomy Textbook. English edition with latin nomenclature. First edition. 2019. ISBN 978-0-7020-6760-0