Gamma radiation - physical nature, spectrum area
Physical nature[edit | edit source]
- γ radiation is one of the two main types of electromagnetic ionizing radiation (the other being X-rays ). X-rays as well as γ radiation are characterized by a dual character , i.e. that they have the properties of both electromagnetic waves and particles of zero rest mass. It is stated that γ radiation has a shorter wavelength than X-ray radiation, but their source is more important for determination , which for γ radiation is the atomic nucleus and the radioactive transformations taking place in it.
γ radiation is the most penetrating of all types of radioactive radiation, but it can be weakened by a thick layer of material containing the nuclei of heavy elements, such as lead . So the intensity will drop, but the radiation will never be completely absorbed. From a physical point of view, it is electromagnetic radiation with high energy.
Since photons , the energy of electromagnetic radiation divided into quanta, have no electric charge, γ radiation does not deviate from its original direction in either an electric or magnetic field ; it just distracts.
Spectrum area[edit | edit source]
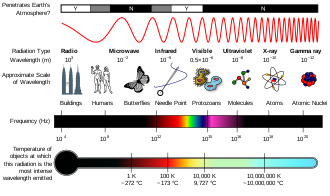
- The spectrum of electromagnetic radiation extends on one side of the spectrum into the radio wave range and on the other into the γ radiation range, whose wavelengths are shorter than 0.1 nm . So it lies beyond UV and X-rays .
Links[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- NAVRÁTIL, Leoš – ROSINA, Jozef. Medicínská biofyzika. 1. edition. Grada, 2005. 524 pp. ISBN 80-247-1152-4.
External links[edit | edit source]
- REICHL, Jaroslav – VŠETIČKA, Martin. Encyklopedia fyziky [online]. [cit. 2015-11-29]. <http://fyzika.jreichl.com/main.article/view/805-zareni-gama>.