Inguinal canal
The inguinal canal , or canalis inguinalis, is a 4–5 cm slit in the lower part of the abdominal wall. It lies above the league. inguinale in places where the bundles of the obliquus internus abdominis and transversus abdominis muscles no longer reach . Here, the abdominal wall is formed only by the aponeurosis of the obliqui externi abdominis muscle , the transverse fascia and the parietal peritoneum .
Contents of the inguinal canal[edit | edit source]
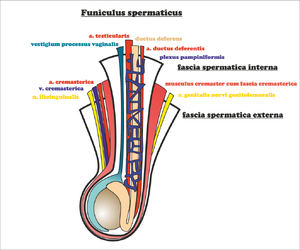
In men, it passes through the canalis inguinalis funiculus spermaticus (during intrauterine development, the testicles descend through the canal to the scrotum together with the peritoneal cavity - proc. vaginalis peritonaei ), in women , lig. teres uteri . In both sexes, the ilioinguinalis nerve (ventral from the funiculus or ligament - often pierces the aponeurosis of the oblique muscle outside the anulus inguinalis superficialis ) and the genitalis n. genitofemoralis (dorsomedially from the funiculus or ligament) also pass through here.
The inguinal canal begins deep in the anulus inguinalis profundus , then runs above the lig. inguinale Pouparti obliquely mediocaudally and into the subcutaneous opening in the anulus inguinalis superficialis .
Anulus inguinalis superficialis (subcutaneus)[edit | edit source]
It is an opening in the aponeurosis musculi obliqui externi abdominis (it projects onto the inner surface of the abdominal wall into the fossa inguinalis medialis ).
Boundaries[edit | edit source]
- Craniomedially : crus mediale – attaches to the tuberculum pubicum (continues to the other side as lig. inguinale reflexum Collesi );
- caudolaterally : crus laterale – merges with the lig. inguinal ;
- laterally : fibrae intercrurales – run arcuately from the ligaments. inguinale perpendicular to both crura;
- medially : lig. inguinale reflexum – attaches to the linea alba , or is a continuation of the bilateral crus mediale .
Anulus inguinalis profundus (praeperitonaealis)[edit | edit source]
It is not a true opening - it is the place where the fascia transversalis is funneled into the inguinal canal and continues as the fascia spermatica interna .
Boundaries[edit | edit source]
- Cranially : the lower edge of the transversus abdominis muscle ;
- caudally : lig. inquinale ;
- medially : lig. interfoveolare (strengthening of the transverse fascia given by the pull of the ductus deferens , which wraps around the lig. interfoveolare ), vasa epigastrica inferiora (branches of the a. iliaca externa ) run behind it ;
- laterally : the angle where the bundles of the transversus abdominis muscle start from the lig. inguinal .
Walls of the inguinal canal[edit | edit source]
- Ventrally : aponeurosis musculi obliqui externi abdominis ;
- dorsally : fascia transversalis (bridging the gap between the lower edge of the obliquus internus + transversus abdominis and lig. inguinale ), is strengthened in the lig. interfoveolare and in the falx inguinalis ;
- cranially : the caudal edges of the obliquus internus and transversus abdominis muscles and their fused tendons continuing into the tendo conjunctivus , which runs along the outer edge of the attachment of the recti abdominis muscle to the pecten ossis pubis ;
- caudally : lig. inguinale Pouparti .
The section of the wall above the lig. inguinale[edit | edit source]
It is formed only by the transverse fascia.
Division by the course of the leagues. interfoveolar to:[edit | edit source]
- lateral - anulus inguinalis profundus (in the fossa inguinalis lateralis , it is the inner gate of an indirect inguinal hernia - hernia inguinalis indirecta );
- medial - trig. inguinale Hesselbachi (in the fossa inguinalis medialis , is the inner gate of a direct inguinal hernia – hernia inguinalis directa ).
Hesselbachi's trigonum inguinale is thus a weak spot of the abdominal wall bordered by thickened strips of transverse fascia ( lig. interfoveolare , falx inguinalis ) and ligamentum inguinale .
Links[edit | edit source]
Related articles[edit | edit source]
External links[edit | edit source]
- Mefanet - Tříselný kanál
- PAVLÍKOVÁ, Lada. Tříšelný kanál [online]. Výukový portál Lékařské fakulty v Plzni [online], ©2009. The last revision 12.10.2011, [cit. 2011-11-27]. <http://mefanet.lfp.cuni.cz/clanky.php?aid=5>.
Source[edit | edit source]
- PASTOR, Jan. Langenbeck’ s medical web page [online]. [cit. 2009]. <https://langenbeck.webs.com/>.