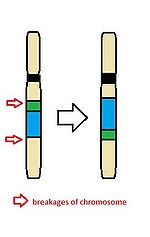
Inversion
From WikiLectures
Inversion is a form of chromosome mutation – structural abnormality.
- Typical for inversion is two breaks in different parts of the chromosome. The newly created segment rearranges itself and is reversed.
- Inversion was discovered in 1921.
- Although we still don´t know why inversion exists, we know that it is the most important mechanism of reorganizing the genome.
- We recognize 2 types of inversion:
- pericentric – causes deletions, insertions or abnormal centromeres, with a breakpoint in each chromosomal arm.
- paracentric – is the more common type, it is less harmful for its carrier as it does not involve the centromere.
- Inversion suppresses the recombination process.
Links[edit | edit source]
Related articles[edit | edit source]
Sources[edit | edit source]
Bibliography[edit | edit source]
- KUMAR, ABBAS, FAUSTO, MITCHELL,, et al. Robbins Basic Pathology. 8th edition edition. 2007. ISBN 978-0-8089-2366-4.