Kidney (SFLT)
Overview of preparations[edit | edit source]
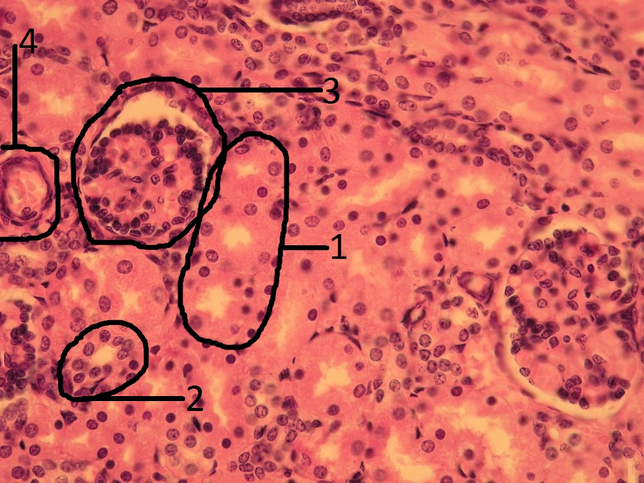
Kidney - hematoxylin-eosin stained[edit | edit source]
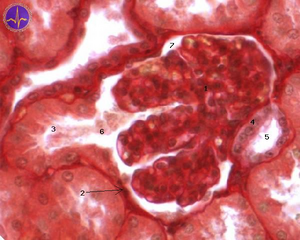
Kidney. The single-layered flat epithelium forms the parietal sheet of Bowman's capsule. The nuclei of the epithelial cells are sheathed, the cytoplasm is hardly visible. Inside Bowman's capsule is the glomerulus - a club of blood capillaries - covered by the visceral leaf of Bowman's capsule. Around the renal corpuscle (glomerulus + Bowman's pouch) we see proximal and distal tubules.
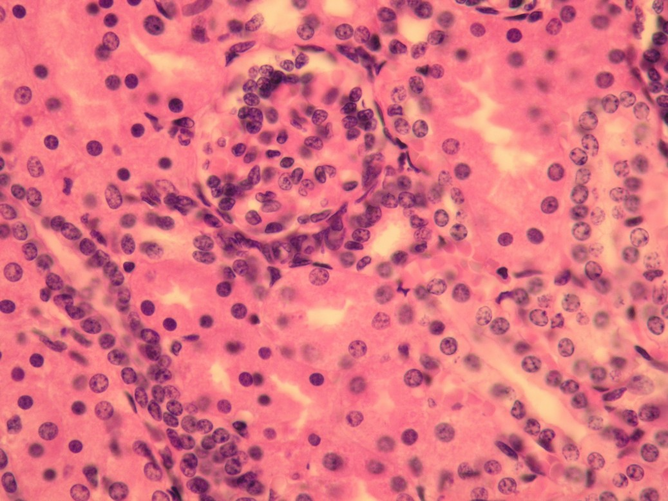
Kidney cortex - hematoxylin-eosin stained I[edit | edit source]
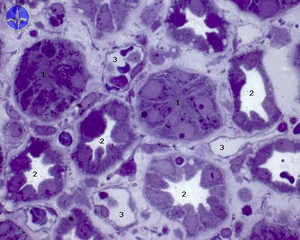
You can see the renal corpuscles, proximal and distal tubules.
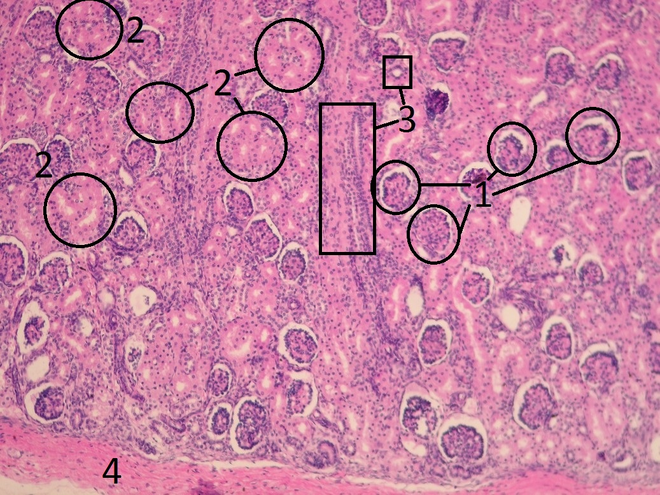
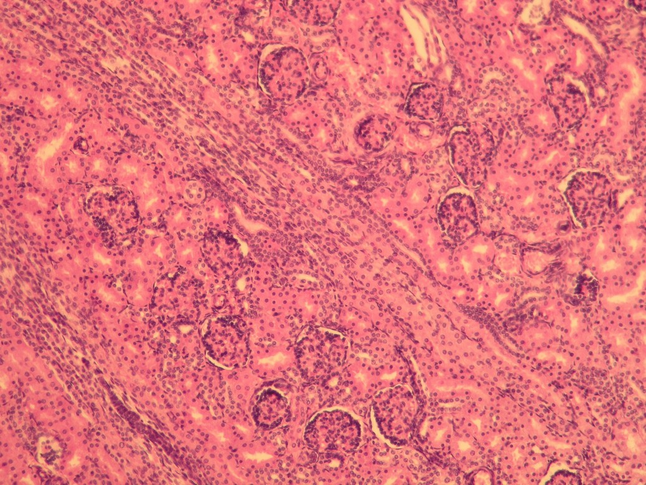
Kidney cortex - hematoxylin-eosin stained II[edit | edit source]
In addition to the renal corpuscle (Bowman's poudre) there are proximal tubules (eosinophilic - pink) with fewer nuclei and obscured lumina. These cells are involved in reverse resorption (they have a brush border on the apical surface at the base of the mitochondria and cytoplasmic folds with Na/K ATPase). Distal tubules are smaller and have a free lumen. They resorb only water and ions, so they have only a baso-lateral labyrinth. In the distal duct near the glomerulus, cells are specialized to detect urine composition (macula densa). They are taller with oval nuclei.
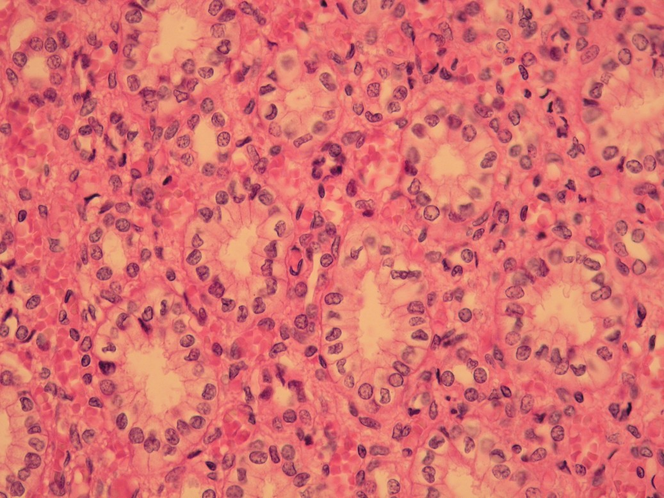
Kidney marrow - hematoxylin-eosin stained[edit | edit source]
In the marrow we see collecting ducts (higher light epithelium) and thin segments of the Henle's villi (flat epithelium).
Kidney (a)[edit | edit source]
View of the arrangement of the cortex of the kidney. The renal corpuscles are superimposed (gradual development of new generations of nephrons). The striae medullares (collecting ducts that connect to the nephrons) run into the cortex.
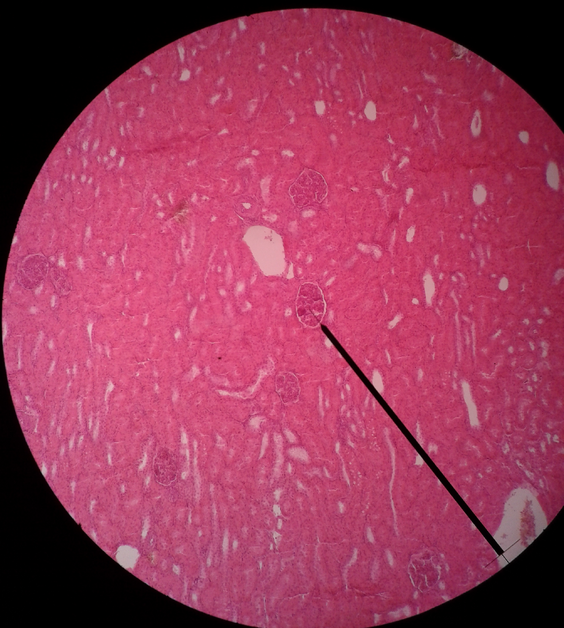
Kidney (b)[edit | edit source]
Kidney at low magnification. The basic structural unit of the kidney is the nephron = renal corpuscle, proximal tubule, thin segment of Henle's duct, distal tubule. The arrow points to the renal corpuscle.
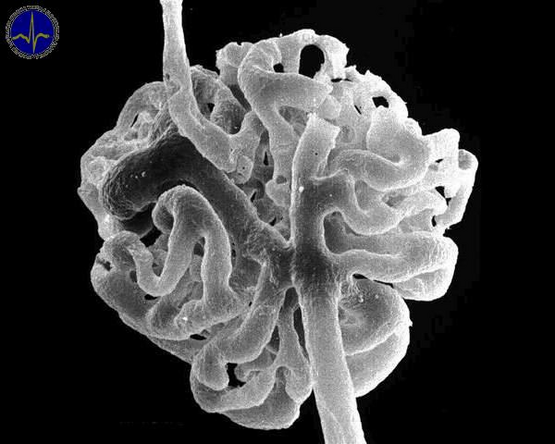
Glomerulus - electronogram and other preparations[edit | edit source]
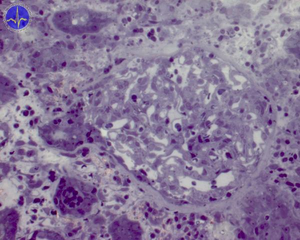
Clubbing of the hair cells, the thicker feeding arteriole glomerularis afferens is visible, the weaker protruding arteriole glomerularis efferens.