Lipids (1. LF UK, NT)
They are natural non-polar compounds that are insoluble in water, but are soluble in non-polar solvents.
Importance of lipids[edit | edit source]
- they are one of the basic components of food, they serve as a source and reserve of energy (38kJ/g)
- structural function - they are part of biomembranes (eg: double layer of phospholipids -> form micelles)
- protective function - they cover some organs and thus protect them from shock
- thermal insulation
- solvents of non-polar vitamins (A, D, E, K)
- precursors
Divisions[edit | edit source]
Simple[edit | edit source]
they contain only the lipid part
- triacylglycerols are the most abundant in the human diet
- waxes (animal, vegetable)
Composite[edit | edit source]
obsahují lipidovou a nelipidovou část
- they contain a lipid and a non-lipid part
- glycoacylglycerols - contain a carbohydrate component
- are part of plant membranes
- phosphoacylglycerols - are part of biological membranes and lipoproteins
- their molecule is amphipathic
- sphingolipids - their basis is a compound that contains the 18-carbon amino alcohol sphingosine
- they are further divided into sphingomyelins containing ceramide and choline, these include cerebrosides and gangliosides containing carbohydrate and sialic acid - they are amphipathic and are found in the brain and nerves
Derived[edit | edit source]
- terpenes
- steroids
Higher fatty acids[edit | edit source]
They are the basic component of lipids. They have a high number of C, a high number of non-polar bonds and only one functional group - COOH, which is polar. They are unbranched, have a hydrophobic character and a cis arrangement that is natural in nature and our body can break it down.
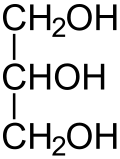
Glycerol[edit | edit source]
=propane-1,2,3-triol, glycerin
It is a sweet viscous liquid, infinitely miscible with water.
Source of dietary fat[edit | edit source]
extraction of crude fats and oils, sources
- vegetable – pressing, extraction
- animal – smelting, extraction
Vegetable fats and oils[edit | edit source]
Refining
- slime removal (hydration), vegetable slimes, proteins, their complexes - lecithin
- deacidification (neutralization) – acid salts
- whitening – carotenoids , chlorophylls
- deodorization – tocopherols , sterols
Classification[edit | edit source]
By consistency
- oils (liquid)
- drying - linen
- semi-drying - sunflower/soybean
- non-drying - olive
- fats (plastic, mushy) – lard
- waxes (hard, non-greasy) – beeswax
By structure
- fatty acids and their soaps R-[CH2]n-COOH
- homolipids (esters of fatty acids with alcohols)
- monohydric alcohols (waxes)
- aliphatic (cerides)
- CH3-[CH2]25-OH... ceryl alcohol (beeswax)
- H3-[CH2]15-OH... hexadecan-1-ol, cetyl alcohol (cetaceum)
- alicyclic (steroids) - esters of sterols (cholesterol), triterpene alcohols
- aliphatic (cerides)
- dihydric alcohols (glycols), Alkoxylipids: 1-Alkoxypropane-2,3-diols Chimyl alcohol


- trihydric (glycerol)
 fats and oils
fats and oils - polyhydric alcohols:
- monohydric alcohols (waxes)
- heterolipids 0.5–2%
- glycerol , MK, another component
- phospholipids (MK esters)

- lipid sulfates (MK esters)

- sulfolipids

- lipamides (MK amides)

- serinol
 , ceramides
, ceramides  , cerebrosides
, cerebrosides 
- complex lipids
- proteolipids ( lipoproteins )
- glycolipids (cerebrosides)
- mucolipids (sialoglycosphingolipids = gangliosides)
Links[edit | edit source]
Related articles[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ws:Lipidy (1. LF UK, NT)
- Maxdorf. Velký lékařský slovník [online]. [cit. 2016-11-09]. <http://lekarske.slovniky.cz/pojem/sfingolipidy>.
- JANATOVÁ, Markéta. Metabolismus lipidů a steroidů [online]. [cit. 2016-11-09]. <https://el.lf1.cuni.cz/p6dp3dd8fm5/?account-id=7&principal-id=8587330&session=breezfn9563te4p3zv6i4>.
- DAVÍDEK, Jiří. 3. LIPIDY [online]. [cit. 2012-03-11]. <https://el.lf1.cuni.cz/p60846053/>.