Lung (SFLT)
Lungs - alveoli[edit | edit source]
Description: The barrier between air and blood is formed by a single-layered flat epithelium (type 1 pneumocytes), a basement membrane (fused laminae basales of both epithelia) and the endothelium of a somatic capillary (with continuous endothelium). The inner surface of the alveolus is covered with surfactant, which is produced in type 2 pneumocytes.
Lungs - alveoli and bronchiolus[edit | edit source]
Description: The bronchiole wall (diameter is less than 5 mm) is lined with multi-row to single-layered cylindrical epithelium with cilia, or only cubical epithelium with cilia in the smallest bronchioles. Terminal brochioles also contain Clara cells. The lamina propria is very thin, the wall is further made up of smooth muscle and elastic and collagen fibers. Cartilage, seromucinous glands, and lymphatic tissue are no longer present in the bronchioles. 1 - bronchiolus, 2 - alveoli, 3 - vessel.
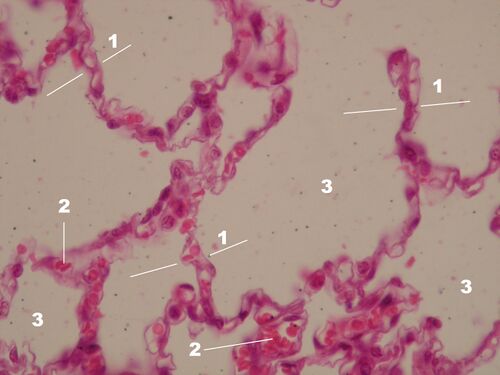
Pulmonary alveoli HE[edit | edit source]
Description: The interalveolar septum is formed by two layers of flat epithelium (pneumocyte type 1 and 2), between which lies interstitial tissue supplying capillaries, typical tissue cells (fibroblasts, macrophages), elastic, collagen and reticular fibers. Each septum is common to the neighboring alveoli, the capillary network is in their closest neighborhood. Alveolar capillaries form the richest capillary network in the body. 1 - interalveolar septum, 2 - erythrocytes in the capillary, 3 - air space (alveolus lumen).
Lung HE - alveolar macrophages[edit | edit source]
Description: Alveolar macrophages (dust cells) in the lung tissue accumulate dust particles that they cannot break down (hence the dark color), they also absorb pathogens and dead cells. They are in the alveoli and terminal airways without cilia.
Lung HE - alveolar macrophages[edit | edit source]
Description: After accumulation, alveolar macrophages (dust cells) either move into the airways lined with ciliated epithelium and are removed with the mucus film, or they migrate to the tissue in the lung parenchyma, where they remain stored, or they are transported by the lymphatics to of regional nodes - this is how anthracotic lymph nodes are formed.
HE lungs - alveoli and interalveolar septa[edit | edit source]
Description: 1 - interalveolar septum, 2 - alveolar macrophage (dust cell), 3 - alveolar lumen (air space).
Electronogram - blood-air barrier[edit | edit source]
Description: P1 - type 1 pneumocyte, E - endothelial cell, BM - their fused basal laminae, Er - erythrocyte.
Electronogram - alveolus wall and blood-air barrier[edit | edit source]
Description: A - alveolar space, C - capillary lumen (above with erythrocyte), P1 - type 1 pneumocyte, P2 - pneumocyte 2 .type (nucleus), Mv - microvilli (microvilli) on the surface of type 2 pneumocyte, L - lamellar bodies with newly synthesized surfactant, E - endothelial cell, NE - endothelial cell nucleus, TJ - tight junction, BM - basement membrane, F - alveolar septum fibroblast, S - surfactant.