Myeloarchitectonics of the cerebral cortex
From WikiLectures
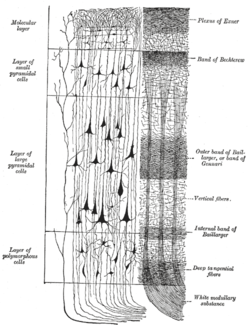
Myeloarchitectonics is a method by which we study the structure of cortical areas of the brain. This method monitors the distribution and course of myelinated nerve fibers in the cerebral cortex. Fibers perpendicular to the surface of the cerebral cortex are referred to as radii (they reach up to the third layer of the cerebral cortex), fibers parallel to the surface of the cortex are called striae (they occur in different densities). The myeloarchitectonics of the cerebral cortex is best stained by the luxol blue. With myeloarchitectonics, we display the cerebral cortex with five strips and one ray.
- Exner strip - in the area of the arachnoid and pia mater
- Bechtěrev's strip - in the area of the lamina molecularis
- external Baillarger strip - in the area of the lamina granularis interna
- internal Baillarger strip – in the area of the lamina pyramidalis interna
- Meynert's strip - in the area of the lamina multiformis
- fibrae radiales – extend up to the 3rd layer, perpendicular to the surface of the cortex
Links[edit | edit source]
Related articles[edit | edit source]
External links[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- JUNQUEIRA, L. Carlos – CARNEIRO, José – KELLEY, Robert O. Junqueira's Basic Histology: Text and Atlas. 1. in Czechia edition. H & H, 1997. 502 pp. ISBN 80-85787-37-7.