Spermatic cord
From WikiLectures
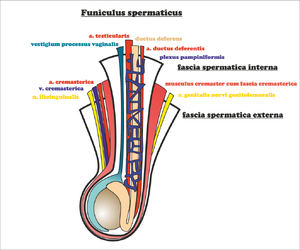
Funiculus spermaticus Structures of the funiculus spermaticus
| Bordered dorsally | tunica dartos, fascia spermatica, m. cremaster + fascia cremasterica, fascia spermatica interna |
|---|---|
| Bordered ventrally | tunica dartos, fascia spermatica, m. cremaster + fascia cremasterica, fascia spermatica interna |
| Builds on | cauda epididymis |
| Content | testicular artery, testicular nerve plexus, pampiniformis venous plexus; ductus deferens, arteria dustus deferentis, nerve plexus of the ductus deferentis |
The spermatic cord ( funiculus spermaticus ) is a bundle of structures found in the male that runs from the cauda epididymis in the scrotum through the inguinal canal to the abdominal cavity.
Sheats[edit | edit source]
The sheaths of the spermatic cord are identical to the sheaths of the testis (except for the tunica vaginalis testis). They arose as derivatives of the abdominal wall during the descent of the testicles. Between the individual layers of the spermatic cord we can find the ramus genitalis nervi genitofemoralis and in the course of the inguinal canal n. ilioinguinalis and a. cremasterica.
- tunica dartos
- fascia spermatica externa
- m. cremaster in its fascia cremasterica
- fascia spermatica interna
Contents[edit | edit source]
- vestigium processus vaginalis peritonei
- lymphatic vessels
ventrally:
- a. testicularis (branch of aorta abdominalis)
- nerve plexus testicularis
- venous plexus pampiniformis
dorsally:
- ductus deferens
- a. ductus deferentis (branch of a. iliaca interna)
- nerve plexus deferentialis
Links[edit | edit source]
Related Articles[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ČIHÁK, Radomír. Anatomie 2. 2. edition. Grada, 2002. 488 pp. ISBN 80-247-0143-X.
- HERÁČEK, Jiří – URBAN, Michael. Urologie pro studenty [online]. Androgeos, ©2012. [cit. 2012-04-05]. <http://www.urologieprostudenty.cz>.
