Stanovení glukózy v moči
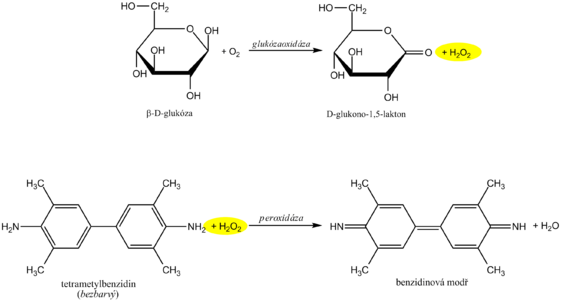
Diagnostic strips for the detection of glucose in urine are based on the principle of enzymatic reactions with glucose oxidase and peroxidase (same principle as the determination of glycemia ). D -glucose is oxidized by oxygen using glucose oxidase to form D -glucono-1,5-lactone and hydrogen peroxide. In a subsequent peroxidase reaction, hydrogen peroxide oxidizes tetramethylbenzidine or another chromogen to a colored product. The light yellow color of the reaction surface changes to blue-green when positive. The test is specific for D -glucose, other sugars do not give a positive reaction.
High concentrations of reducing agents such as ascorbic acid slow down the development of color and can lead to falsely lower results. In these cases, it is recommended to repeat the analysis at least 10 hours after vitamin C withdrawal. Conversely, false positive results may be due to the presence of peroxidase substrates or oxidizing agents in the sampling vessel (eg H 2 O 2 , Persteril ®, chloramine B ). Urine glucose determination should be performed rapidly to avoid bacterial contamination or urine should be stored at 4 ° C.
Interference with ascorbic acid is a common source of false negatives. Urine test strips from some manufacturers are therefore modified so that the reaction zone is at least somewhat resistant to ascorbic acid. Some diagnostic strips also have an ascorbate detection zone to alert you to false negatives.
Glucosuria is most often accompanied by an increase in glycaemia above the so-called renal glucose threshold (around 10 mmol / l). Glucose, which normally filters through the glomerular membrane, is in such a high concentration in primitive urine that it is not enough to be resorbed in the tubules and reaches the final urine. Glucosuria with normal glycemia indicates a disorder of tubular transport mechanisms - we are talking about renal glucosuria .