Submandibular triangle, carotid triangle
|
This article was marked by its author as Under construction, but the last edit is older than 30 days. If you want to edit this page, please try to contact its author first (you fill find him in the history). Watch the discussion as well. If the author will not continue in work, remove the template Last update: Sunday, 01 Dec 2024 at 11.35 pm. |
Submandibular triangle, carotid triangle[edit | edit source]
The triangles of the neck are topographic areas which are bounded by the neck muscles.
Sternocleidomastoid muscle divides the neck into 2 major neck triangles: anterior triangle and posterior triangles, each of them containing a few subdivisions.
The importance of the triangles are due to their content, as they contain the neck structures including glands, nerves, vessels and lymph nodes.
Both triangles discussed here are subdivisions of the anterior triangle of the neck.
The anterior triangle[edit | edit source]
Is further subdivided by the hyoid bone, suprahyoid and infrahyoid muscles into 4 different triangles. The anterior triangle is situated at the front of the neck and has the following borders:
1. Superiorly- the inferior border of mandible.
2. Laterally- the anterior border of sternocleidomastoid.
3. Medially - sagittal line down the midline of the neck.
4. Floor- visceral fascia of the neck.
5. Roof- investing fascia of the neck.
6. Apex- jugular notch.
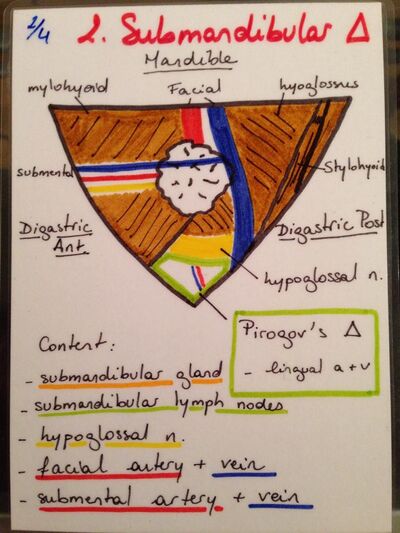
The submandibular triangle[edit | edit source]
Located below the body of mandible and above both bellies of the digastric muscle. Its Boundaries are as follows:
1. Anteriorly- anterior belly of digastric muscle.
2. Posteriorly- posterior belly of digastric muscle and stylohyoid muscle.
3. Superiorly- body of mandible bone.
4. Apex- intermediate tendon of digastric muscle.
5. Floor- Mylohyoid and hypoglossal muscles.
6. Roof- skin, fascia and platysma muscle.
Content of the submandibular triangle[edit | edit source]
1. Submandibular gland
2. Submandibular ganglion
3. Submandibular duct
4. Submandibular lymph nodes
5. Facial artery
6. Facial vein
7. Submental artery
8. Submental vein
9. Lingual artery
10. Lingual vein
11. Lingual nerve
12. Mylohyoid nerve
13. Hypoglossal nerve
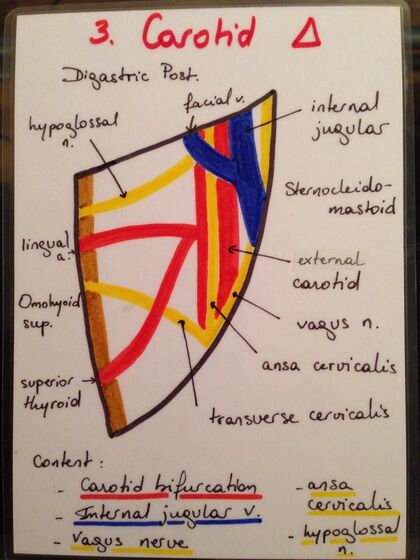
The carotid triangle[edit | edit source]
Located beneath the submandibular triangle, ventral to sternocleidomastoid muscle. Its boundaries are as follows:
1. Anteriorly- omohyoid muscle superior belly.
2. Superiorly- posterior belly of digastric muscle and stylohyoid muscle.
3. Laterally- medial border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
4. Inferiorly- omohyoid muscle superior belly.
5. Floor- hypoglossal muscle, thyrohyoid muscle parts, inferior and middle pharyngeal constrictors.
6. Roof- deep and superficial fascia of the neck, skin, platysma.
Content of the carotid triangle:[edit | edit source]
The carotid triangle contains the internal carotid sheath (internal jugular vein, common carotid artery, vagus nerve).
1. Common carotid artery (bifurcates at level C4).
2. Internal jugular vein
3. Hypoglossal nerve
4. Superior root of Ansa cervicalis
5. Vagus nerve
6. External carotid artery
7. Superior thyroid artery
8. Lingual artery
9. Facial artery
10. Facial vein
11. Retromandibular vein
12. Lingual vein
13. Superior thyroid vein
14. Sympathetic trunk (superior cervical ganglion)
15. Accessory nerve
16. Lateral group of deep cervical lymph nodes
Pirogoff’s triangle[edit | edit source]
A sub triangle located within the submandibular triangle. Its borders are as follows:
1. Anteriorly- tendon of digastric muscle
2. Posteriorly- tendon of digastric muscle
3. Superiorly- hypoglossal nerve.
Content of Pirogoff’s triangle:
1. Lingual artery
2. Lingual vein
Beclard’s triangle[edit | edit source]
A sub triangle located within the submandibular triangle, where the lingual artery could be found. Its borders are as follows:
1. Superiorly- posterior belly of digastric muscle
2. Posteriorly- posterior margin of hyoglossus muscle
3. Inferiorly- greater horn of hyoid bone.
Sources[edit | edit source]
Stingl, J., Grim, M., & Druga, R. (2012). ''Regional anatomy''. Galen.