Toxic substances
|
This article was marked by its author as Under construction, but the last edit is older than 30 days. If you want to edit this page, please try to contact its author first (you fill find him in the history). Watch the discussion as well. If the author will not continue in work, remove the template Last update: Friday, 12 May 2023 at 10.44 pm. |
Toxic substances present real risks:
- causing food intolerance ( intolerance ), toxic for certain individuals,
- causing intoxication , toxic for all individuals.
Substances causing food intolerance:
- allergies (immunological reactions), allergens (immunogens), (do not) induce IgE formation,
- celiac disease , gluten-free diets (<100 mg/kg gliadin dry weight),
- intolerance (non-immunological manifestations), metabolic disorders, hypersensitivity (anaphylaxis), aversion (idiosyncrasy),
- lactose intolerance, foods with a low content (<10 g/kg), lactose-free (100 mg/kg),
- phenylketonuria , hydrolysates without Phe,
- favism, broad bean ( Vicia faba ).
https://www.wikiskripta.eu/w/Soubor:Toxiny-vicin.jpg
Toxins and other substances causing intoxication[edit | edit source]
Classification:
- by structure,
- physical properties,
- by origin (plant, animal),
- by effects,
- main groups of toxins,
- alkaloids,
- saponins,
- cyanogens,
- glucosinolates,
- lectins,
- estrogenic substances,
- phototoxic substances,
- amino acids,
- biogenic amines.
Antinutritional and toxic substances of legumes:
- protease and amylase inhibitors,
- α-galactosides,
- substances causing favism,
- lectins ,
- cyanogenic glycosides,
- estrogens ,
- saponins ,
- lathyrogens.
Toxic substances of higher mushrooms:
- proteins ,
- peptides ,
- amino acids ,
- amines,
- hydrazines,
- alkaloids ,
- terpenoids.
Alkaloids[edit | edit source]
Classification:
- true alkaloids (N-heterocycles, derived from amino acids),
- pyridine (nicotine) and tobacco,
- piperidine and pepper,
- pyrrolizidines and senecias (necines),
- quinolizidine and. lupins,
- quinoline and cinchona barks,
- pseudoalkaloids (N-heterocycles, derived from other precursors),
- purine a. coffee, tea, cocoa,
- terpenoid (glycoalkaloids) a. potatoes, tomatoes,
- protoalkaloids (not N-heterocycles, derived from amino acids),
- capsaicinoids and peppers.
Pyridine alkaloids[edit | edit source]
Nicotine and minor alkaloids (~20 compounds):
- tobacco (obligation to indicate content in tobacco products, warnings).
Piperidine alkaloids[edit | edit source]
Piperine, homologs, geometric isomers, related substances, pepper (hot substances)
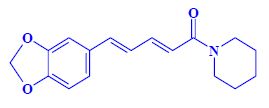
Pyrrolizidine alkaloids[edit | edit source]
Many related esters (mono-, di-, macrocyclic), hepatotoxic substances.
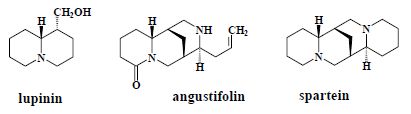
Quinolizidine alkaloids[edit | edit source]
A number of related compounds, lupine.
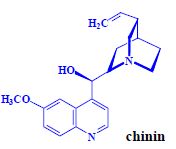
Quinoline alkaloids[edit | edit source]
Contents in pod.

Legislation: additive, alcoholic beverages 300 mg/l, non-alcoholic (tonics) 75 mg/l (teratogenicity)
Purine alkaloids[edit | edit source]
a number of related compounds, coffee, tea, cocoa (chocolate), mate, guarana.
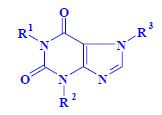
- caffeine R 1 = R 2 = R 3 = CH 3
- theobromine R 1 = H, R 2 = R 3 = CH 3
- theophylline R 1 = R 2 = CH 3 , R 3 = H
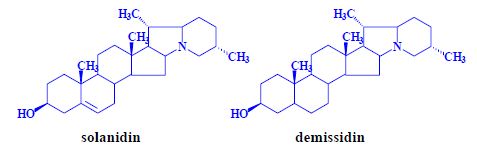
Steroidal glycoalkaloids[edit | edit source]
- a number of related compounds, potatoes, tomatoes, eggplant,
- heteroglycosides, aglycone, sugar.
Potatoes[edit | edit source]
- α-solanine = solanidine + β-solatriose,
- α-chaconine = solanidine + β-chacotriose,
- distribution,
- legislation: 200 mg/kg.
Tomatoes[edit | edit source]
- tomatine = tomatidine + β-lycotetraose
- legislation: 200 mg/kg, teratogenicity
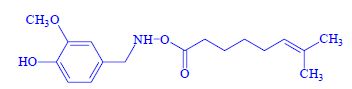
Capsaicinoids[edit | edit source]
capsaicin, homologues, paprika (hot substances):
- the effect of technological processing,
- capsaicin, (E)-8-methyl-N-vanillylnon-6-enamide .
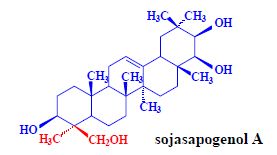
Saponins[edit | edit source]
a number of related compounds, foods of plant origin:
- heteroglycosides, aglycone, sugar,
- aglycon = sapogenin (sapogenol),
- triterpene alcohols,
- sterols (4-demethylsterols).
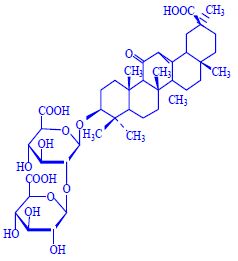
Biological effects:
- hemolysis of erythrocytes , other cells, damage to the intestinal mucosa.
Properties
- toxicity to cold-blooded animals,
- bitter taste,
- detergent effects, emulsion (o/w),
- fungicidal, antioxidant, anticarcinogenic, anticholesterolemic effects.
Use
- foaming agents (cosmetics),
- emulsifiers (cosmetics),
- sweeteners (glycyrrhizin, licorice: 0.2−5.6% saponins).
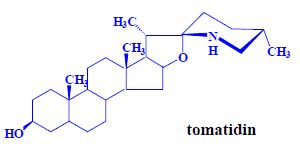
Cyanogenic glycosides[edit | edit source]
- a number of related compounds, foods of plant origin,
- HCN content in cyanogens,
- heteroglycosides, aglycone, sugar,
- aglycone = 2-hydroxynitrile (cyanohydrin),
- 2-hydroxy acid nitrile.
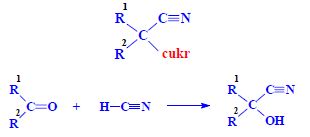
Substituents - Chirality:
- aliphatic – acetone, methyl (ethyl) ketone,
- aromatic – benzaldehyde.
Sugar
- usually Glu,
- genciobiosis disaccharides etc.
Properties
- decomposition (β-glucosidase) → HCN, toxicity (inhibition of cytochrome oxidase in the respiratory chain),
- acute intoxication, chronic intoxication (cassava, cassava).
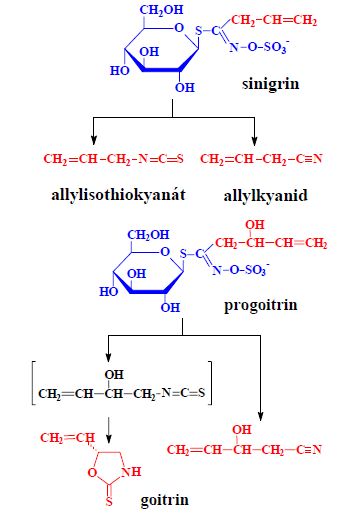
Glucosinolates[edit | edit source]
- thioglucosides (glucosides of mustard oils), a number of related compounds, foods of plant origin (cruciferous plants),
- names and structure,
- dominant glucosinolates in vegetables,
- heteroglycosides, aglycone, sugar, aglycone = thiohydroxamate-O-sulfonate, counterion K+
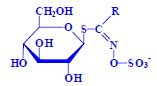
Substituents
- aliphatic,
- aromatic,
- heterocyclic.
Sugar
- exclusively Glc.
Properties
- decomposition (myrosinase) → isothiocyanates, nitriles, etc.,
- toxicity, isothiocyanates and goitrin strumogenic, nitriles hepatotoxic.
Plant phenols[edit | edit source]
estrogenic substances[edit | edit source]
- phytoestrogens - foods of plant origin,
- isoflavones,
- content in soybeans.
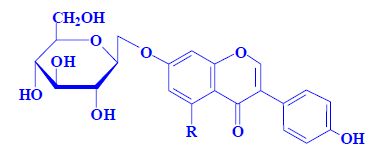
- daidzin, R = H aglycon daidzein
- genistin, R = OH aglycon genistein
- soybeans (0.13−0.42%)
- pterocarps,
- lignans.
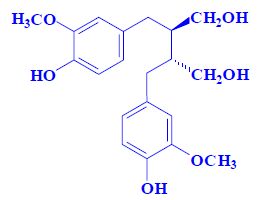
- content in food
- coumestrol − sprouting − soybeans
- secoisolariciresinol − flax seeds
- mycoestrogens,
- xenoestrogens.
Properties
- simultaneously useful and harmful.
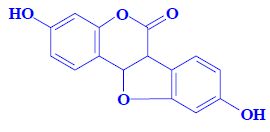
Phototoxic substances[edit | edit source]
- coumarins,
- furanocoumarins,
- foods of plant origin.
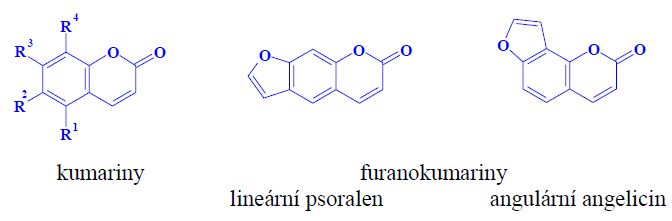
Properties
- phototoxicity (sensitivity of non-pigmented skin, association with skin cancer, acute dermatitis),
- phytoalexins (phytonicides, plant antibiotics, pesticides), blastocolins (inhibits seed germination),
- antimicrobial and other effects.
Phototoxic pigments[edit | edit source]
- hypericin (St. John's wort), fagopyrin (buckwheat).
Lectins (phytohemagglutinins)[edit | edit source]
- foods of plant origin (seeds and other parts)
Proteins with a non-catalytic center:
- merolectins (1 center, catalytic no),
- hololectins (2 centers, no catalytic),
- chimerolectins (1−2 centers, catalytic yes).
Soy lectin
- metalloprotein, 120 kDa, hololectin, N-acetyl-D-galactosamine binding.
Properties
- precipitation of erythrocytes, interaction with sugars in glycoproteins and glycolipids of membranes (plant protection mechanism against predators, parasites),
- toxic intravenously, some orally, some not at all, some probiotics (garlic).
Amino acids[edit | edit source]
Lathyrogens:
- foods of plant origin (seeds of vetiver and peas),
- amino acids (peptides, nitriles) -3-(N-oxalyl)-2,3-diaminopropanoic acid
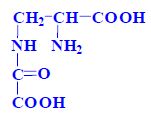
Properties
- structural form with proteinogenic amino acids, metabolic disorders,
- deformation of the lower limbs (osteolathyrism), damage to blood vessels (angiolatyrism), disorders of the nervous system (neurolathyrism), humans, mainly farm animals.
Biogenic amines:
- precursors,
- aliphatic, aromatic, heterocyclic bases with biological activity, fermented and microbially degraded foods of plant and animal origin
Emergence
- from amino acids by microorganisms
- histamine (His)
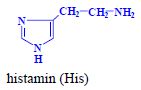 , cadaverine (Lys)
, cadaverine (Lys) 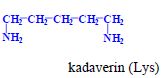
- histamine (His)
Properties
- tissue hormones (allergic reactions, anaphylactic shock)
- psychoactive and vasoactive substances
Content
- changes in salami
Links[edit | edit source]
Internal links[edit | edit source]
- Natural toxic substances (1. LF UK, NT)
Source[edit | edit source]
- DAVIDEK, Jiří. 12. NATURAL ANTINUTRITIONAL AND TOXIC SUBSTANCES [online]. [feeling. 2012-03-13]. < https://el.lf1.cuni.cz/p30693038/ >