Xeroderma pigmentosum
From WikiLectures
Xeroderma Pigmentosum
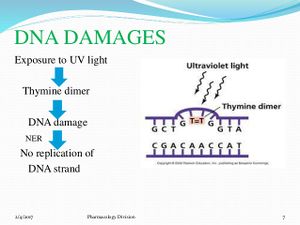
Xeroderma pigmentosum is a rare autosomal recessive disorder of DNA repair, where the ability of the DNA to repair the damage caused by Ultraviolet light (from sun or any other sources) is deficient
Exposure to sunlight causes severe damage to the skin cells and can also lead to multiple basal cell carcinomas. In advanced stages, metastatic malignant melanoma and squamous cell carcinoma are the 2 most common cause of death in patients with Xeroderma pigmentosum. In extreme cases, exposure to sunlight is forbidden and such patients are termed "Moon children"
Signs and Symptoms:
1. Severe sunburn when exposed to only small amounts of sunlight. These often occur during a child's first exposure to sunlight. 2. Development of many freckles at an early age 3. Rough-surfaced growths (solar keratoses), and skin cancers 4. Eyes that are painfully sensitive to the sun and may easily become irritated, bloodshot and clouded 5. Blistering or freckling on minimum sun exposure 6. Telangiectasia also known as Spider veins 7. Limited growth of hair on chest and legs 8. Scaly skin 9. Xeroderma also known as Dry skin 10. Irregular dark spots on the skin 11. Corneal ulcerations
Diagnosis:
1. Severe sunburn after first exposure to sunlight. 2. Conclusively diagnosed by measuring the DNA repair factor from skin or blood samples.
Treatment:
1. Avoiding exposure to sunlight (wearing protective clothing, sunscreen, etc,.) 2. Treating keratosis with cryotherapy or fluorouracil.