Brown fat (slide)
From WikiLectures
Brown fat[edit | edit source]
Overview[edit | edit source]
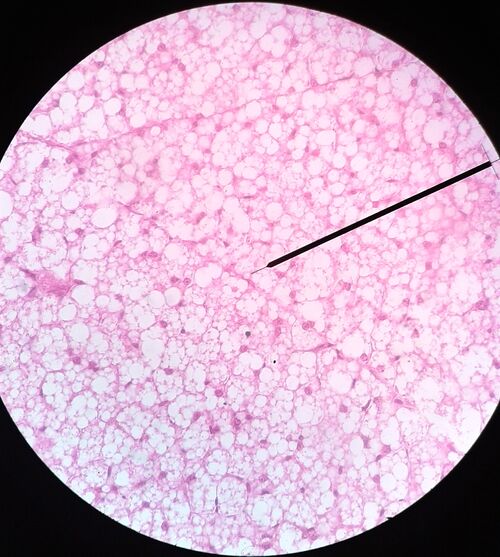
Slide 1[edit | edit source]
Title Brown fat HE
Description: Brown Adipose Tissue cells - multilocular contain multiple lipids droplets and large numbers of mitochondria. In humans, brown fat is important after birth for thermoregulation (non-shivering thermogenesis). Brown fat cells probably persist in the body throughout life, but the volume of brown adipose tissue decreases relatively. Thus, in adulthood, white fat. significantly predominates.
Slide 2[edit | edit source]
Title: Brown fat
Description: Cells of brown adipose tissue at higher magnification. Cells have a nucleus in the center and multiple lipid droplets.
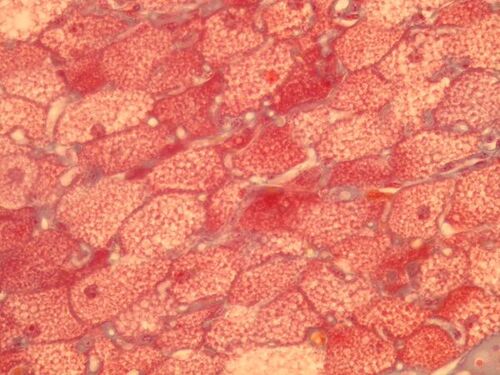
Slide 3[edit | edit source]
Title: Brown fat AZAN
Description: Brown fat cells - detail.
Binders[edit | edit source]
Desmogenous ossification (slide)
Enchondral ossification (slide)
Links[edit | edit source]
Module Cellular Foundations of Medicine (3. LF)