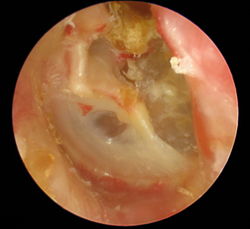
Cholesteatoma
From WikiLectures
Cholesteatoma (cholesteatoma) is a false tumor of fat cells, cholesterol, fatty acids and keratinized epithelia. It has enzymes on the surface → it destroys the surroundings. It is most often found in the middle ear or in the area of the mastoid process .
It grows locally destructively. It oppresses the surrounding structures and causes their atrophy to necrosis (destroys the auditory ossicles and the surrounding bone).
Etiology[edit | edit source]
The formation of cholesteatoma is interpreted as:
- Migration of the epidermis into the middle ear after perforation of the eardrum,
- a diverticulum of the epidermal layer of the tympanic membrane,
- true epidermoid from fragments of ectoderm during development of the ear canal.
It can be congenital or acquired (more common).
- Secondary infection is quite common (Pseudomonas aeruginosa).
Clinical picture[edit | edit source]
- Inflammation (there is also a non-inflammatory form of genuine cholesteatoma) – chronic ear infections;
- There may be a perforation of the eardrum,
- ear discharge,
- pain;
- ± symptoms of spread to the inner ear, meninges, venous drainage;
- conductive hearing loss, deafness, balance disorders, dizziness.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
- Surgical – removal of cholesteatoma.
Complications[edit | edit source]
- Untreated, it causes chronic inflammation of the middle ear, damage to the facial nerve, meningitis, inflammation of intracranial veins, deafness, …
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
Recurrences are possible after surgical removal.
Links[edit | edit source]
Related Articles[edit | edit source]
Source[edit | edit source]
- WIKIPEDIA.INFOSTAR.CZ,. wikipedia.infostar.cz [online]. [cit. 2011-12-26]. <http://www.brana.cz/5/c/ch/cholesteatoma.html>.
- VELKÝ LÉKAŘSKÝ SLOVNÍK,. Velký lékařský slovník [online]. [cit. 2011-12-26]. <http://lekarske.slovniky.cz/pojem/cholesteatom-ucha>.