Epithelial Tumors of the Oral Cavity
From WikiLectures
Epithelial tumors of the oral cavity can be divided into benign and malignant.
Epithelial benign tumors[edit | edit source]
Squamous cell papilloma[edit | edit source]
- It occurs mainly on the palate, buccal mucosa and lips.
Epithelial malignant tumors[edit | edit source]
Carcinoma of the Lip[edit | edit source]
- Occurrence mainly on the lower lip.
- Mostly in older men.
- It metastasizes to the submandibular and submental nodes very late.
- Diagnosis very good.
- At first a small hardening of the lip, then the separation of epithelia, the formation of a crust, under the crust a ulcer forms.
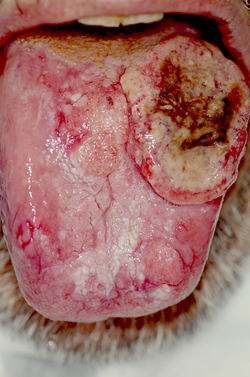
Carcinoma of the Tongue[edit | edit source]
- The most malignant tumor of the oral cavity.
- It metastasizes to the lymphatic nodes and the lungs.
- It occurs at the edges of the middle third of the tongue, tip and at the base.
- It grows rapidly in depth.
- Three times more common in men.
- At first only hardening of the tongue, later ulcer, pain, grows in cauliflower style and endophytic.
Carcinoma of the Base of the Oral Cavity[edit | edit source]
- Very common.
- Hardened ulcer, usually located laterally from the middle part of the base.
- It grows exophytically and endophytically.
- It often metastasizes contralaterally to the regional nodes.
Carcinoma of the Buccal Mucosa[edit | edit source]
- Ulceration with hardened base.
- Mainly in the molar area.
- Often exophytic growth.
Carcinoma of the Palate[edit | edit source]
- It is more common on the soft palate.
- Has the appearance of an ulceration.
Gingival Carcinoma[edit | edit source]
- It grows exophytically and endophytically.
- It often destroys the bone.
- In the maxilla, it can grow into the maxillary cavity.
Verrucosal Carcinoma[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
Literature[edit | edit source]
- LIŠKA, Karel. Orofaciální patologie. 1. vydání. 1983.