Eye (biophysics)/Disorders of the eye
Physiological state - the optical system of the eye is able to create a sharp image of an object on the retina.
For this, two conditions must be met:
- The image of a point is a point
- Disorder of this condition = astigmatism. Astigmatism is caused by the asymmetry of the optical power of the eye (the cause is most often the cornea, which is irregularly curved), so the rays do not intersect in one focal point, but in two line segments .
- The image is created exactly on the retina (in a healthy, emmetropic eye)
- Far point - the distance at which the eye can see clearly without accommodation (normally infinity).
- If the distant point is at a finite distance, depending on the location of the distant point, we distinguish two types of "spherical ametropia":
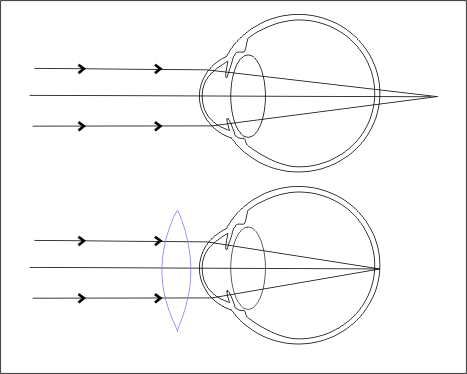
- The distant point is at a finite distance 'in front of the eye, i.e. such an eye only sees clearly objects at a distance smaller than the far point, because at greater distances the image of the object is formed in front of the retina (optical power is too great). High myopia is the most common risk for retinal detachment.
- The distant point is at a finite distance behind the eye, the image of objects placed at infinity is formed behind the retina (the optical power is too small).
The eye changes its optical power through the curvature of the lens. The degree of curvature is the so-called near point' = the distance that the eye sees sharply at maximum accommodation of the lens. The ability to accommodate decreases with age. If the distance of the near point is extended beyond the conventional visual distance (d = 25cm), this condition manifests itself in eye fatigue when reading - presbyopia.
Defects are corrected using glasses'' or contact lenses.
Correction:
- myopia - 'distractions
- hypermetropia – clutches
- presbyopia - conjuncts
- only regular astigmatism can be corrected - using cylindrical glasses - we try to make the two foci merge.
Links[edit | edit source]
Related articles[edit | edit source]
External links[edit | edit source]
- Eye defects - advice, information
- Kymplová Jaroslava: Eye and eye defects. Multimedia support for the teaching of clinical and medical fields :: Portal of the 1st Faculty of Medicine of Charles University in Prague [online] 2/19/2008, last update 2/19/2008 [cit. 2011-12-22] Available from WWW:<https://portal.lf1.cuni.cz/clanek-810-oko-a-ocni-vady>. ISSN 1803-6619