Organum vestibulocochleare (SFLT)
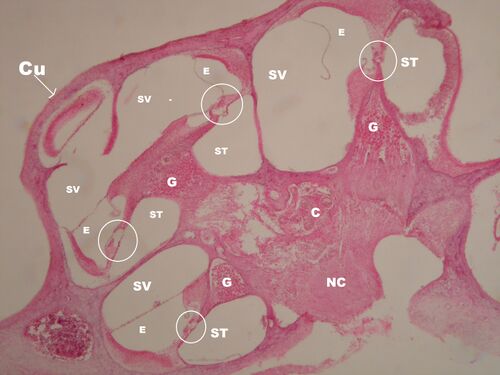
Cochlear Section - Overview (HE)[edit | edit source]
Description: C – blood vessels, Cu – cochlea cupula, E – endolymphatic space = ductus cochlearis (scala media), G – ganglion cochleare, NC – nervus cochlearis, perilymphatic spaces: ST – scala tympani, SV – scala vestibuli.
Cross-section through one turn of the cochlea - detail of the previous preparation (HE)[edit | edit source]
Description: 1 – membrana basilaris, 2 – membrana vestibularis Reissneri, 3 – tunnel spaces of Corti, 4 – membrana tectoria, 5 – stria vascularis, 6 – ligamentum spiralis, 7 – prominentia spiralis, 8 – limbus spiralis, 9 – ganglion cochleare, 10 – efferent nerve fibers from ganglion cochleare, future nervus cochlearis, 11 – lamina spiralis ossea, 12 – bony cochlea, E – endolymphatic space = ductus cochlearis (scala media), P – perilymphatic space: ST – scala tympani and SV – scala vestibuli.
Ductus cochlearis (scala media) – detail (HE)[edit | edit source]
Description: 1 – organ of Corti, 2 – membrana basilaris, 3 – crista spiralis, 4 – lamina spiralis ossea, 5 – membrana tectoria, 6 – limbus spiralis, 7 – dashed line represents the membrana vestibularis Reissneri, which was not preserved in this preparation, 8 – stria vascularis, 9 – prominentia spiralis, 10 – sulcus spiralis externus, 11 – capillaries in the stria vascularis (the stria vascularis of the inner ear is the only epithelium with blood vessels, otherwise the epithelium is avascular tissue), 12 – ligamentum spirale, 13 – bony cochlea, E – endolymphatic space = ductus cochlearis (scala media), P – perilymphatic space: ST – scala tympani, SV – scala vestibuli.
Organ of Corti - detail (HE)[edit | edit source]
Description: 1 – membrana basilaris, 2 – tunnel spaces in the organ of Corti, 3 – lamina spiralis ossea containing afferent nerve fibers from the ganglion cochleare, 4 – membrana tectoria, 5 – inner hair cell, 6 – outer hair cells, 7 – outer phalanx cells, 8 – other supporting cells, E – endolymphatic space = ductus cochlearis (scala media), P – perilymphatic space of scala tympani.
Stria vascularis of the inner ear – an example of epithelium with a vascular supply (HE)[edit | edit source]
Description: 1 – ligamentum spiralis, 2 – capillaries in stria vascularis, 3 – bony cochlea, 4 – prominentia spiralis, 5 – lumen of scala media (= ductus cochlearis).
[edit | edit source]
Description: E – endolymphatic space, P – perilymphatic space, p – perilymph in the tunnel of Corti, SV – stria vascularis produces endolymph, bm – basilar membrane (does not have a barrier function, therefore there is also perilymph in the tunnel of Corti), rm – reticular membrane (barrier endolymph in the scala media – perilymph in the tunnel of Corti), Reissner's vestibular membrane (endolymph barrier in the ductus cochlearis – perilymph in the scala vestibuli).
Section through the cochlea - course of ganglia and nerves (overview, HE)[edit | edit source]
Description: E – endolymph, P – perilymph, K – bony cochlea (fibrous bone), G – ganglion cochleare,
NC – nervus cochlearis, ls – ligamentum spirale, sv – stria vascularis, in ovals – organs of Corti
Ganglion spirale – detail (HE)[edit | edit source]
Description: l – lamina spiralis ossea has two strips between which afferentation takes place, af – afferent nerve fibers from ganglion cochleare to hair cells, G – ganglion cochleare, NC – nervus cochlearis, K – bony cochlea (fibrous bone), Ls – limbus spiralis, mt – tectorial membrane.
Vestibular apparatus - crista ampullaris detail (HE)[edit | edit source]
Description: E – endolymph, P – perilymph, VB – hair cells of the vestibular apparatus, PL – planum semilunare
(dark) forms the endolymph, NV – nerve fibers of the future vestibular nerve, K – bony labyrinth.