Principles of obesity treatment
From WikiLectures
Obesity is a chronic disease characterized by an increase (hypertrophy and hyperplasia) adipose tissue due to a positive energy balance.
Therapy[edit | edit source]
- Diet-based therapy: it involves adjusting the ratio of consumed macronutrients (proteins : fats : carbohydrates = 15: 30: 55), reducing the amount of fatty foods, increasing the intake of fiber, and adhering to a meal plan with 4 -5 meals a day.
- Physical activity: 30-40 minutes of exercise 3-4 times per week is recommended. The patient does not have to lose weight to the ideal weight according to BMI, but a loss of 10% of the original weight is sufficient to significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Behavioral psychotherapy
- Pharmacotherapy:
- Anorexics (reduce appetite) - catecholamine (Adipex), serotonergic drugs, sibutramine (no longer sold)
- Thermogenic drugs (increase energy expenditure) - Elsinor powders
- Substances that affect the absorption of fats in the gut (lipase inhibition) - Orlistat. There is a risk of diarrhea after eating a meal containing a relatively high amount of fats.
- Surgical therapy - bariatric surgery is performed in patients with the most severe form of obesity, which can render them immobile. These surgeries can be either restrict the stomach volume (restrictive) or reduce the area for nutrient absorption (malabsorptive).
- Gastric bandage (laparoscopic adjustable gastric bandage, LAGB) is a laparoscopic surgical technique involving the placement of a silicone ring that tightens the stomach at the top, essentially creating a "second pylorus" and reducing the stomach volume. This will lead to a feeling of satiety much earlier in the meal (i.e., with a smaller amount of food).
- Gastric tubulation (sleeve gastrectomy)
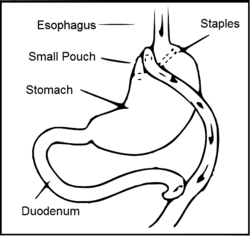
- Gastric bypass: the result of this procedure is the bypass of the majority of the stomach and the initial portion of the intestine, leading to partial malabsorption: less nutrients are absorbed from consumed food.
- Biliopancreatic diversion (shrinkage of the stomach and formation of a bypass between the stomach and the distal half of the ileum).
- Gastric balloon (endoscopic insertion of a balloon into the stomach. This method is rarely used today).
In 2009, about 800 bariatric procedures were performed in the Czech Republic. In 2010, over 1000 were performed. Today, surgical treatment of obesity is the treatment with the highest success rate. Pharmacotherapy is less effective.
Links[edit | edit source]
Related Articles[edit | edit source]
- Obesity
- Obesity (pediatrics)
- Diseases resulting from nutrient deficiencies or excesses
- Risk factors for cardiovascular diseases
- Carbohydrates in food
- Fats in food
- Proteins in food
- Nutrition recommendations
Literature[edit | edit source]
- PASTOR, Jan. Langenbeck's medical web page [online]. [cit. 2010]. <http://langenbeck.webs.com>.
- ČEŠKA, Richard, et al. Interna. 1. vydání. Praha : Triton, 2010. 855 s. ISBN 978-80-7387-423-0.