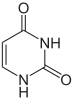
Pyrimidines
Pyrimidine is a six-membered heterocyclic compound that includes nitrogenu heteroatoms in the 1 and 3 positions. The system of conjugated bonds determines its aromatic character.
Chemical properties[edit | edit source]
Pyrimidine has ``basic properties due to the free electron pairs of both nitrogens. At the same time, however, the energy of the π-electrons decreases and the molecule is less prone to electrophilic substitution and, conversely, more prone to nucleophilic substitution. The first nitrogen and carbons 4-6 come from aspartate', the second carbon comes from HCO3-, the second carbon comes from amide of the glutamine group. The pyrimidine precursor carbamyl phosphate is formed from glutamine and HCO3-, another precursor is aspartate itself. "Carbamyl phosphate" and "aspartate" by connecting with "N-carbamylaspartate" give the formation of "dihydroorotate". Further reactions gradually produce ``uridine-5'-monophosphate (UMP), the main intermediate of pyrimidine synthesis, which is formed by decarboxylation. ``UMP-synthase ensures the last two steps leading to pyrimidine formation.
Pyrimidine derivatives[edit | edit source]
Pyrimidine is the basis of some nitrogenous bases: thymine, uracil and cytosine. These are attached via an N-glycosidic bond to ribose or deoxyribose and form nucleosides. Thymine is found in DNA, while uracil is found in nature only in RNA. Both are complementary to adenine, to which they are linked by two hydrogen bonds. Cytosine is complementary to guanine and forms three hydrogen bonds.
[[File:Thiamin.svg|thumb|right|200px|Vitamin B1 (thiamin)]In addition to the main base, minor bases can also occur (e.g. 5-methylcytosine', 5-hydroxymethylcytosine',...).The pyrimidine derivative is also barbituric acid, whose derivatives have sedative effects.
Pyrimidine is also part of vitamin B1 and of course purine.
Links[edit | edit source]
Related Articles[edit | edit source]
External links[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
- MATOUŠ, Bohuslav, et al. Basics of medical chemistry and biochemistry. 1. edition. Prague : Galen, 2010. 540 pp. pp. 44. ISBN 978-80-7262-702-8.
- MURRAY, Robert Kincaid – BENDER, David A – BOTHAM, Kathleen M, et al. Harper's Illustrated Biochemistry. 5. edition. Prague : Galen, 2012. 730 pp. pp. 307. ISBN 978-80-7262-907-7.This article has been translated from WikiSkripta; ready for the editor's review.