Staining in light microscopy
When staining preparations for light microscopy, it is always an interaction of a certain dye and some tissue component. Various dyes stain tissues due to their affinity for acid or base. Accordingly, they are called eosinophilic (acidophilic) - for their affinity to basic structures in cells (e.g. mitochondria , lysosomes , agranular endoplasmic reticulum , cytoplasm ) and basophilic - for their affinity to acidic structures (they are acidic because they contain genetic information formed by nucleic acids) (e.g. ribosomes , granular endoplasmic reticulum and cell nucleus). Staining is divided into clear and selective. The goal when staining preparations is to achieve contrast between individual tissue components.
Clear coloring[edit | edit source]
Through this staining, we obtain general information about the entire preparation. The dyes for clear staining include Hematoxylin-eosin, Wigert van Gieson, Masson's trichromes and AZAN.
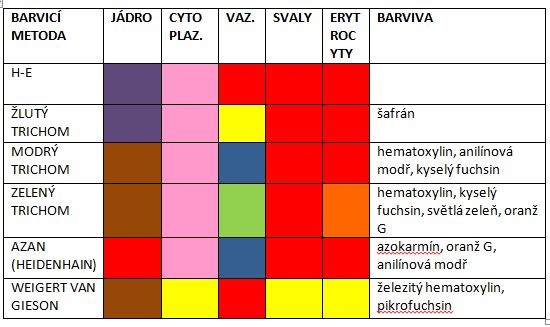
Hematoxylin-eosin (HE)[edit | edit source]
This is the best-known example of clear coloring. Hematoxylin is basic, eosin is an acidic dye. While hematoxylin stains the nuclei blue-violet, eosin stains the cytoplasm pink.
- See the Hematoxylin-eosin staining page for more detailed information .
Weigert van Gieson[edit | edit source]
This dye stains the nuclei brown-black, the ligament red and the muscle yellow.
Masson's trichrome[edit | edit source]
We distinguish three types of trichromes according to the color that the collagen fiber is dyed. Nuclei are usually stained with hematoxylin.
Green[edit | edit source]
It distinguishes between collagen fibers (green) and elastic fibers (purple) in the ligament. Nuclei are stained brown. Cytoplasm of cells is stained red by green Masson's trichrome. We can also easily distinguish erythrocytes , which are colored orange.
Blue[edit | edit source]
Blue trichrome stains the ligament blue and the nuclei brown because iron hematoxylin is used. Muscles dye red.
Yellow[edit | edit source]
Yellow trichrome colors the fiber in yellow, the core in dark blue. We can also clearly distinguish the cytoplasm, which is stained red with this dye.
AZAN[edit | edit source]
Like trichrome blue, it stains collagen fibers blue (these dyes are often confused), but the nuclei stain red, due to the azocarmine used.
Selective staining[edit | edit source]
Selective staining selects and marks only certain structures in the preparation . For example, we can obtain an overview of the presence of reticular or elastic fibers, determine the presence of acidic mucopolysaccharides or glycogen. Selective dyeing belongs to the group of special dyes. Overview of dyes and the structures that are dyed with them:
Mucicarmine[edit | edit source]
Mucicarmine is a selective dye that can stain mucus.
Orcein[edit | edit source]
This dye is of natural origin. Dyes elastic fibers red-brown.
Alcian blue[edit | edit source]
Staining with Alcian blue and Azocarmine Stains acid mucopolysaccharides blue. It only works in acidic pH.
Best's crimson[edit | edit source]
This dye is used to detect glycogen at a site of high concentration.
Szpielmayer's hematoxylin[edit | edit source]
It can stain myelin sheaths .
Congo red[edit | edit source]
Congo red is used to detect amyloidosis .
Oil red[edit | edit source]
We can stain neutral lipids with this dye.
Sudanese black[edit | edit source]
Sudan black is one of the best-known dyes that stain neutral lipids.
Heidenhain[edit | edit source]
The result is black cardiomyocytes.
Links[edit | edit source]
Related articles
- Staining methods (1. LF UK)
- Hematoxylin-eosin staining
- Histochemistry
- Principles of conventional histochemistry in light microscopy
- Preparation of histological specimen
References
- WAGNER, Philip. Basics of dyeing [online]. [feeling. 2011-10-22]. < http://www.upol.cz/fileadmin/user_upload/LF-kliniky/histologie/studijni_materialy/zaklady_barveni_v_histologii.pdf >.
- LÜLLMANN-RAUCH, Renate. Histology. 3rd edition. 2012. ISBN 978-80-247-3729-4 .
- VAJNER, Ludek. Microscopic techniques [lecture on the subject of Histology, field of General Medicine, 2nd Faculty of Medicine, Charles University]. Prague. 21/06/2011.



