Sternal puncture (pediatrics)
From WikiLectures
Indication[edit | edit source]
- Disorders of the hematopoietic system,
- oncological diseases: leukemia, lymphomas, neuroblastoma,
- thesaurismosis,
- diseases of the macrophage system: histiocytosis.
Contraindications[edit | edit source]
- There are no contraindications to the collection of bone marrow (in the case of the inflammation swelling process skin above the injection site, we choose a different collection site).
Bone marrow aspirate is used for morphological examination of blood cell developmental lines, ie for differential cell budgeting in panoptic staining, and for special examinations. Special tests include histochemical staining for enzyme activity or PAS reaction for glycogen content.
In recent years, the basis of differential diagnosis has become immunological examination (presence of CD-antigen on the surface of white cells) and cytogenetic examination.
Procedure[edit | edit source]
- Bone marrow is collected in children up to 2 years of age tibia, in children> 2 years of age sternum (it can also be obtained from other places, eg from the anterior and posterior ridges of the hip bone, from the projections of the bodies vertebrae or from femur),
- adequate analgesia is suitable before collection,
- the skin at the injection site is widely disinfected as before surgery, we work sterile in surgical gloves,
- infiltrate the subcutaneous tissue at the injection site with a thin needle approx. 2 to 3 ml of 1% Mesocaine as close as possible to periosteum
- after spraying we wait 1 to 2 minutes,
- for puncture we use special needles for bone marrow aspiration, 18 to 19 G for larger and 21 to 22 G for smaller children,
- the needle has a mandrel and a screw-on, adjustable stop,
- set the needle stop to the estimated distance (approx. 2 cm for larger and 1 cm for smaller children); the stop serves to prevent unwanted abnormally deep punctures,
- we penetrate the skin with the needle, most easily from an oblique angle, then we set the needle perpendicular to the bone:
- at the tibia in the upper third on the front wall, between the fingers of the other hand, with which we fix the tibia by holding both krists,
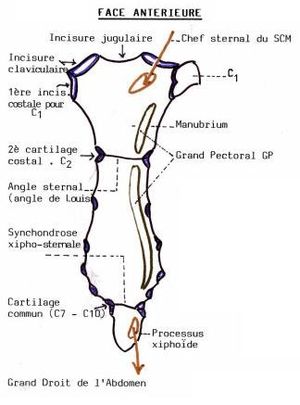
- at the sternum on the manubrium sternum at the imaginary intersection of the perpendiculars of the center of the jugula and the 2nd intercostal space,
- with a gentle helical movement at a constant gentle pressure, we insert the needle into the bone marrow, the resistance of the bone is noticeably relaxed after reaching the marrow, the needle holds itself firmly in the bone,
- remove the mandrel and aspirate the bone marrow with a 20 ml syringe,
- we end the aspiration as soon as a few drops (max. 0.5 to 1 ml) of bone marrow appear in the syringe, which is macroscopically indistinguishable from blood,
- remove the needle and the syringe, cover the injection site aseptically and compress with gentle pressure for 3 to 5 minutes,
- immediately after aspiration, the bone marrow is sprayed onto the prepared degreased slide and coated on at least another 5 to 10 slides (for immunological or cytogenetic examination it is necessary to aspirate more marrow and inject the aspirate into non-coagulating media),
- in some special indications (especially in oncohematology) the so-called "trepanobiopsy" is also performed, when the marrow is not aspirated, but a complete marrow sample with a bone matrix is obtained.
Complications[edit | edit source]
- Bleeding in thrombocytopenia or coagulopathy.
Links[edit | edit source]
Source[edit | edit source]
- HAVRÁNEK, Jiří: Sternální punkce. (upraveno)