Tumors of the larynx
From WikiLectures
Both benign and malignant tumors can occur in the larynx. Non-tumor lesions can also occur here based on chronic inflammation or traumatization. Epithelial tumors overwhelmingly dominate over mesenchymal tumors.
Benign tumors and non-cancerous lesions[edit | edit source]
Nodulus vocalis[edit | edit source]
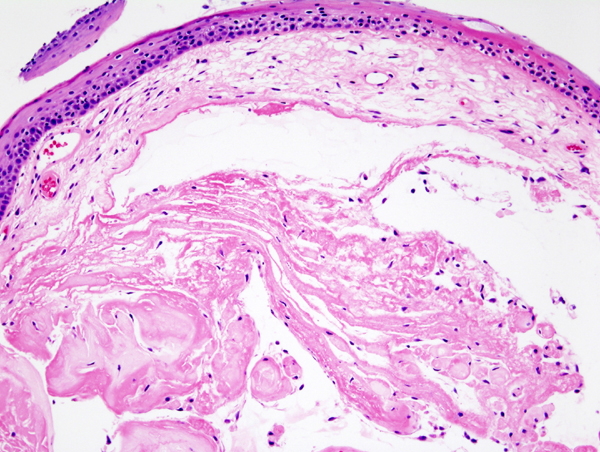
- Also a singing nodule, it arises bilaterally on the vocal cords during chronic abuse of the voice.
- The histological picture shows edema and myxoid transformation of the ligament in Reinke's space (the space between the squamous epithelium of the vocal cord and the vocal ligament).
Vocal polyp[edit | edit source]
- Most often occurs unilaterally after short-term voice switching.
Squamous papilloma of the larynx[edit | edit source]
- Benign epithelial tumor caused by HPV virus type 6 and 11 infection. Less favorable are HPV 16 and 18.
- Juvenile type – often multiple (papillomatosis), papillomas scattered anywhere in the larynx and in the trachei, there is a risk of airway obstruction.
- Adult type – mainly solitary, greater risk of malignancy.
- Histologically, koilocytosis with hyperplasia epidermis is demonstrable.
Malignant tumors[edit | edit source]
Laryngeal carcinoma[edit | edit source]
- Malignant epithelial tumor of the larynx.
- Histologically, it is most often a squamous cell (squamous) carcinoma.
- Tumor proliferation develops from the stage of mild, moderate and severe dysplasia, through carcinoma in situ to the image of invasive squamous carcinoma.
- Carcinoma grows in either an exophytic (verrucous carcinoma) or endophytic (conventional carcinoma) manner.
- According to localization, the tumor is divided into "supraglottic, glottic and infraglottic type".
- The glottic type has the best prognosis, the infraglottic type has the worst prognosis (in the initial stage it is asymptomatic and metastasizes to the mediastinum and regional nodes).
- Glottic carcinoma most often arises in the ligamentous part of one vocal cord and spreads to the other vocal cord through the anterior commissure, it manifests clinically very soon.
- Supraglottic carcinoma arises from islands of squamous epithelium of the epiglottis.
- Infraglottic carcinoma is very rare.
Etiology - particularly smoking cigarettes, drinking hard alcohol or air pollution, viral etiology also plays a role here.Epidemiology - this is the most common malignant tumor in the ENT area, it overwhelmingly affects men with a frequency of 9.4 per 100,000, the average age is 60 years.
Clinical signs - hoarseness (especially if it lasts more than 2 weeks), odynophagia, dyspnoea.
Metastasis - cancer metastasizes to regional lymph nodes (especially in the trigonum caroticum).
- Infraglottic carcinoma also metastasizes to the peritracheal nodes, which manifests itself at a very late stage.
- Distant metastases are mainly located in the lungs.
Links[edit | edit source]
Related Articles[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- HYBÁŠEK, Ivan. Ušní, nosní a krční lékařství. 1. edition. Praha : Galén, 1999. ISBN 80-7184-949-9.
- POVÝŠIL, Ctibor – ŠTEINER, Ivo – DUŠEK, Pavel, et al. Speciální patologie. 2. edition. Praha : Galén, 2007. 430 pp. ISBN 978-807262-494-2.