Mesenchymal tumors
Mesenchyme is an embryonic tissue (made up of cells with projections and wide intercellular spaces filled with a thin ground substance). It comes mostly from the mesoderm and gives rise to connective tissues (ligament, cartilage, bone), blood vessels, muscles and hematopoietic tissue.
Mesenchymal tumors usually have a histoid structure (i.e. without an obvious difference between parenchyma and stroma, as the tumor originates from those components that are close to the stroma), the demarcation to the surroundings is often not sharp, even in benign variants.
Classification of mesenchymal tumors[edit | edit source]
- soft tissue tumors: fibroma, lipoma, hemangioma, lymphangioma, myoma...
- bone tumors
According to the starting tissue:
- from fibroblastoid connective tissue (fibroma, myxoma, lipoma, osteoma, chondroma),
- from the endothelium and vascular tissues (hemangioma, lymphangioma),
- from muscle tissue (leiomyoma, rhabdomyoma),
- from the hemopoietic and lymphoreticular system (hemoblastoma, hemoblastosis),
- undifferentiated (spindle cell, round cell, polymorphic).
Benign mesenchymal tumors[edit | edit source]
They grow expansively, do not metastasize, are limited to the surrounding area, mobile in relation to the surrounding tissue, usually painless. Through expansive growth, they can have a destructive or secondary malignant effect (by oppression). Malignant reversal is possible.
Includes:
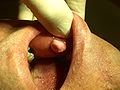
- Fibroma – spherical, grey-pink, harder, circumscribed, usually not encapsulated, several mm to cm, on the tongue, in the subcutaneous tissue.
- Lipoma - soft, yellow, often encapsulated, 1 to several cm, in the subcutaneous tissue.
- Myxoma – gelatinous, less demarcated, recurrent.
- Chondroma – cartilaginous, circumscribed, in bones, tendons.
- Chordoma - soft, translucent, in clivus, several mm.
- Osteoma – bone growth, painless, frontal sinus.
- Osteoid osteoma - hurts, cortex of long bones.
- Hemangioma:
- Lymphangioma - pale yellow, in intestine, cystic - face, neck = hygroma colli cysticum.
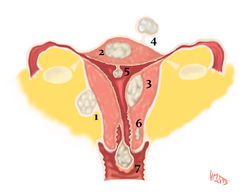
- Leiomyoma - from smooth muscle, spherical, gray-pink, bundle-shaped, circumscribed, solid, uterus, GIT.
- Rhabdomyoma – from striated muscle, in children face, neck, heart, limited.
- Myoblastic myoma – in the tongue, it recurs, there is usually pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia in the epithelium above it.
Complications: oppression of the environment, atrophy (in uterine fibroids, endometrial atrophy and infertility), aesthetics, phonation, intracranial death.
Malignant mesenchymal tumors[edit | edit source]
Malignant mesenchymal tumors are referred to as sarcomas (fish flesh appearance). They grow infiltratively and metastasize mainly hematogenously. The degree of malignancy is determined by the frequency of mitoses, chromosomal atypia, and the presence and extent of necrosis, rather than nuclear and cellular polymorphism. The basic marker is the material of intermediate filaments – vimentin, in muscle cells desmin (and a component of myofilaments).
Includes:
- fibrosarcoma
- chondrosarcoma
- hemangiosarcoma
- leiomyosarcoma
- rhabdomyosarcoma
- osteosarcoma
Links[edit | edit source]
Related Articles[edit | edit source]
- Myxoma
- Lipoma
- Liposarcoma
- Hibernoma
- Hemangioma
- Angiosarcoma
- Lymphangioma
- Leiomyoma
- Leiomyosarcoma
- Rhabdomyoma
- Rhabdomyosarcoma
- Chondroma
- Chondrosarcoma
- Osteoma
- Osteosarcoma
Source[edit | edit source]
- PASTOR, Jan. Langenbeck's medical web page [online]. [cit. 18.04.2010]. <https://langenbeck.webs.com/>.
- STŘÍTESKÝ, Jan. Patologie. 1. edition. 2001. ISBN 80-86297-06-3.