Vulvitis: Difference between revisions
From WikiLectures
(original text is from (https://www.wikiskripta.eu/w/Vulvitis)) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Vulvitis or inflammation of the external genital organs occurs more often in older women, in connection with damage to the superficial layers of the skin, or, on the contrary, in children with neglected hygiene. Normally the skin is very resistant to infection, but the problem arises when a woman is too obese or when the skin is repeatedly injured by scratching or macerated by urine, sweat, etc. Skin resistance also decreases in general metabolic disorders - [[Diabetes Mellitus/type 2|diabetes mellitus]], [[hepatopathy]], [[anaemia]], etc. | |||
== Clinical pattern == | |||
== | * Itching of the external genitalia, burning during and after urination - i.e. pseudodysuria, difficulties during sexual intercourse. | ||
* | |||
== | == Bacterial vulvitis == | ||
* | *[[Folliculitis]], furunculosis - circumscribed form; | ||
* | *[[phlegmon]] - unbounded. | ||
* | *On inspection we see reddened skin, which is further sensitive to touch, warm, swollen. When the hair sacs of the vulva are infected, the infection penetrates into the deeper layers, the so-called furuncles are formed. Furuncles often coalesce and form multiple purulent deposits, even phlegmon. | ||
* | *The solid infiltrate gradually coagulates to form an [[abscess]]. We rarely see this condition today, but if we diagnose it, we must think about possible immune system disorders - AIDS - and we must rule out diabetes mellitus. | ||
* | *With ulcerations we think of syphilitic ulcer (ulcus molle), tuberculous ulcer (ulcus vulvae chronicum), lymphogranuloma venereum. Also, we can sometimes see on the vulva swollen plaques - condylomata lata - representing the second stage of syphilis. | ||
=== | === Inflammation of [[Bartholini's gland]] <small>(Inflammatio glandulae vestibularis majoris seu Bartholini)</small> === | ||
* Inflammation of part or the whole gland; | |||
*begins with inflammation of the duct of the gland, swelling and obstruction of the duct, the contents stagnate, become infected and [[empyema]] develops; if left untreated, the inflammation spreads to the surrounding area and an abscess develops; | |||
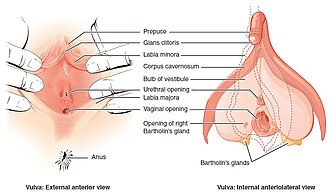
* | * [[File:Vulva Figure 28 02 02.jpg|thumb|Anatomy of vulva]][[retention cyst]] - chronic form, the process is usually unilateral, the thickened duct of the gland is clogged with thick mucus. | ||
* | ;Origins: ''[[Escherichia coli|E. coli]]'', ''[[Chlamydia trachomatis]]'', ''[[Neisseria gonorrhoeae]]'', streptococci, staphylococci. | ||
; | ;Clinical pattern: Pain, swelling of the area, difficulty walking, [[Fever (pediatrics)|fever,]] reddened skin, elevated [[CRP]] and leukocytes. | ||
; | ;Diagnostics: Culture is necessary. | ||
; | ;Therapies: At the beginning conservative - rest, compresses, [[Antibiotics|ATB]], [[analgesics]], in case of development of empyema and abscess surgical intervention is necessary - incision with drainage, chemical extirpation (we suction the contents of the cyst through the incision, then we insert 0.5 cm of AgNO3 (lapis) rods into the abscess cavity, we close the incision with a suture and within 48 h after removing the suture we pull out the wrinkled gland capsule). | ||
; | == Mycotic vulvitis == | ||
== | * Whitish plaques on the vulva, small epithelial defects, itching. | ||
* | |||
== | == Viral vulvitis == | ||
==== Condylomata accuminata ==== | ==== Condylomata accuminata ==== | ||
* | * Warty growths caused by neoncogenic [[papillomaviruses]]; | ||
* virus | *the virus multiplies in the squamous epithelial cells, hence the growths are also found in the [[vagina]] and [[cervix]]. | ||
==== [[ | ==== [[Herpes simplex virus]] ==== | ||
* | * The disease manifests itself after 3-6 days of incubation by small blisters on the labia and in the vagina; | ||
* | *possible bacterial superinfection; | ||
* | *highly infectious fluid oozes after blister rupture. | ||
; | ;Diagnostics: Bacteriological examination, parasitological examination of stool, biochemical, haematological examination. | ||
; | ;Therapy: is determined by the results of the examination - application of anti-inflammatory drugs, [[antifungal drugs]], ointment with [[Corticosteroids|corticosteroids,]] in more severe forms of herpetic infections [[acyclovir]] (administration of the drug must be as soon as possible after seeding). In papillomavirus infections, a 20% solution of podophyllotoxin or trichloroacetic acid, newly - causes local immunoreaction. | ||
<noinclude> | <noinclude> | ||
== Odkazy == | == Odkazy == | ||
=== Související články === | === Související články === | ||
Revision as of 13:47, 2 February 2022
Vulvitis or inflammation of the external genital organs occurs more often in older women, in connection with damage to the superficial layers of the skin, or, on the contrary, in children with neglected hygiene. Normally the skin is very resistant to infection, but the problem arises when a woman is too obese or when the skin is repeatedly injured by scratching or macerated by urine, sweat, etc. Skin resistance also decreases in general metabolic disorders - diabetes mellitus, hepatopathy, anaemia, etc.
Clinical pattern
- Itching of the external genitalia, burning during and after urination - i.e. pseudodysuria, difficulties during sexual intercourse.
Bacterial vulvitis
- Folliculitis, furunculosis - circumscribed form;
- phlegmon - unbounded.
- On inspection we see reddened skin, which is further sensitive to touch, warm, swollen. When the hair sacs of the vulva are infected, the infection penetrates into the deeper layers, the so-called furuncles are formed. Furuncles often coalesce and form multiple purulent deposits, even phlegmon.
- The solid infiltrate gradually coagulates to form an abscess. We rarely see this condition today, but if we diagnose it, we must think about possible immune system disorders - AIDS - and we must rule out diabetes mellitus.
- With ulcerations we think of syphilitic ulcer (ulcus molle), tuberculous ulcer (ulcus vulvae chronicum), lymphogranuloma venereum. Also, we can sometimes see on the vulva swollen plaques - condylomata lata - representing the second stage of syphilis.
Inflammation of Bartholini's gland (Inflammatio glandulae vestibularis majoris seu Bartholini)
- Inflammation of part or the whole gland;
- begins with inflammation of the duct of the gland, swelling and obstruction of the duct, the contents stagnate, become infected and empyema develops; if left untreated, the inflammation spreads to the surrounding area and an abscess develops;
- retention cyst - chronic form, the process is usually unilateral, the thickened duct of the gland is clogged with thick mucus.
- Origins
- E. coli, Chlamydia trachomatis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, streptococci, staphylococci.
- Clinical pattern
- Pain, swelling of the area, difficulty walking, fever, reddened skin, elevated CRP and leukocytes.
- Diagnostics
- Culture is necessary.
- Therapies
- At the beginning conservative - rest, compresses, ATB, analgesics, in case of development of empyema and abscess surgical intervention is necessary - incision with drainage, chemical extirpation (we suction the contents of the cyst through the incision, then we insert 0.5 cm of AgNO3 (lapis) rods into the abscess cavity, we close the incision with a suture and within 48 h after removing the suture we pull out the wrinkled gland capsule).
Mycotic vulvitis
- Whitish plaques on the vulva, small epithelial defects, itching.
Viral vulvitis
Condylomata accuminata
- Warty growths caused by neoncogenic papillomaviruses;
- the virus multiplies in the squamous epithelial cells, hence the growths are also found in the vagina and cervix.
Herpes simplex virus
- The disease manifests itself after 3-6 days of incubation by small blisters on the labia and in the vagina;
- possible bacterial superinfection;
- highly infectious fluid oozes after blister rupture.
- Diagnostics
- Bacteriological examination, parasitological examination of stool, biochemical, haematological examination.
- Therapy
- is determined by the results of the examination - application of anti-inflammatory drugs, antifungal drugs, ointment with corticosteroids, in more severe forms of herpetic infections acyclovir (administration of the drug must be as soon as possible after seeding). In papillomavirus infections, a 20% solution of podophyllotoxin or trichloroacetic acid, newly - causes local immunoreaction.
Odkazy
Související články
- Původci infekcí pohlavního ústrojí ženy
- Vulvovaginitidy
- Nenádorová onemocnění vaginy
- Bakteriální vaginóza
Použitá literatura
Kategorie:Gynekologie
Kategorie:Porodnictví
Kategorie:Patologie
Kategorie:Mikrobiologie