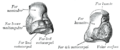
Carpal bones
The carpal bones (ossa carpi) consist of two rows of small bones, each row of four:
- Proximal row – (mediolaterally, ulnoradially) os pisiforme, triquetrum, lunate, scaphoid;
- Distal row – (mediolateral, ulnoradial) os hamatum, capitatum, trapezoideum, trapezoid.
The proximal series participates in radioulnar articulation. The distal ossa metacarpi (metacarpal bones) are attached.
The carpal bone forms the bony base of the carpal tunnel, through which the tendons of m. flexor digitorum superficialis et profundus and the median nerve, which is often oppressed here (carpal tunnel syndrome), pass.
Proximal series[edit | edit source]
Os pisiforme[edit | edit source]
Pisiform bone. It has both the shape and size of a pea grain. It develops as a sesame bone in the tendon of the ulnar flexor of the wrist.
Os triquetrum[edit | edit source]
Triangular bone. It has the shape of an irregular tetrahedron.
Os lunatum[edit | edit source]
Calendula bone. Its shape resembles a crescent.
Os scaphoideum[edit | edit source]
Shuttle-shaped bone (not to be confused with os naviculare on tarsus). Its shape remotely resembles a boat, the depression is reversed medially. It is the largest bone of the proximal series. It bears tuberculum ossis scaphoidei. (unfortunately on the English version of the picture there is just mentioned error - naviculare x scaphoideum)
Distal series[edit | edit source]
Os hamatum[edit | edit source]
Hook-shaped bone. It has a triangular shape. Prominently from it stands out hamulus ossis hamati (hook).
Os capitatum[edit | edit source]
Head bone. The largest carpal bone. The proximal part is called the caput ossis capitati and fits into the proximal series between the os lunatum and os scaphoideum.
Os trapezoideum/Os multangulum minus[edit | edit source]
A small polygonal bone, or scarf-shaped. Its shape resembles the letter L (shoe), in the sagittal cross-section it has the shape of a pyramid turned by the base on the dorsum manus.
Os trapezium/Os multangulum majus[edit | edit source]
Large bone polygonal. It has a similar shape to the os trapezoideum, but it is larger. Laterodorsally, there is a prominent saddle surface for articulation with the first (thumb) metacarpal bone.
ossification[edit | edit source]
Carpal ossifications ossify postnatally in the following order (approximate time of ossification in parentheses):
- Os capitatum (2. m), hamatum (3. m), triquetrum (3. r), lunatum (4. r), scaphoideum (5. r), trapezium (5. r), trapezoideum (6. r), pisiforme (7.–13. r).
Ossification of carpal ossicles is a good indicator of a child's physical maturity.
Pictures[edit | edit source]
Links[edit | edit source]
Related Articles[edit | edit source]
Bibliography[edit | edit source]
- ČIHÁK, Radomír, et al. Anatomie 1. 1. edition. Praha : Grada Publishing, a.s., 2008. 516 pp. vol. 1. ISBN 80-7169-970-5.