Gonosomal recessive inheritance
From WikiLectures
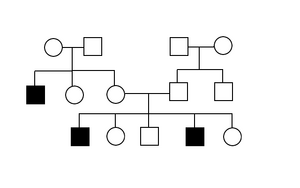
Gonosomal recessive inheritance is the transmission of the observed trait, the allele oh which lies gonosome, namely chromosome X (X-linked inheritance). Few genes are located on the chromosome Y, eg. SRY. The increased pubic hair previously reported as an example of a Y-linked trait (OMIM: 425500), is probably not strongly linked to the Y chromosome.
A typical manifestation is a far greater number of sick men than women, who are overwhelmingly only healthy carriers.
Deviations[edit | edit source]
Some inconsistencies may arise because carriers have different degrees of disease manifestation. It is caused by random lyonization of one of the X chromosomes in each cell of the body. This can occur, for example, in hemophilia.
Examples[edit | edit source]
- Hemophilia A (OMIM: 306700)
- Hemophilia B (OMIM: 306900)
- Color blindness (OMIM: 303800)
- Duchenne muscular dystrophy (OMIM: 310200)
- Becker muscular dystrophy (OMIM: 300376)
Links[edit | edit source]
Related links[edit | edit source]
- Autosomal dominant inheritance
- Autosomal recessive inheritance
- Gonsomal inheritance
- X-linked inheritance
- Y-linked inheritance
- Non-Mendelian inheritance