Diabetes mellitus (pediatrie)
From WikiLectures
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a set of symptoms that includes multiple nosological units.
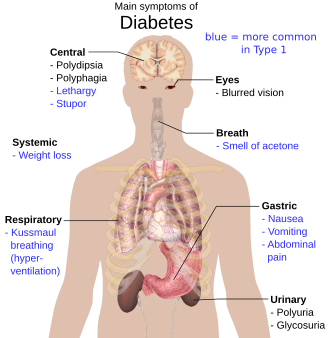
Characteristic symptoms include: hyperglycemia, glycosuria, absolute or relative lack of insulin, risk of late complications due to chronic hyperglycemia.[1]
- Diagnostic criteria of DM
- typical symptoms of diabetes (polyuria, polydipsia, weight loss) and at the same time venous glucose ≥ 11.1 mmol/l at any time during the day;
- or
- fasting blood glucose ≥ 7.0 mmol/l;
- or
- blood glucose ≥ 11.1 mmol/l at the 120th minute oGTT (oral glucose tolerance test).[1]
The most serious acute complication of diabetes is diabetic ketoacidosis - as a result of an absolute or relative lack of insulin, fatty acids are used as a substitute source of energy (ketogenesis):
- pH < 7.30 or HCO3– < 15 mmol/l with hyperglycemia > 12 mmol/l and ketonemia/ketonuria.[1]
Types of diabetes in children and adolescents[edit | edit source]
Milder forms of the disorder:
- impaired glucose tolerance: blood glucose 7.8 – 11.0 mmol/l at the 120th minute oGTT;
- increased fasting blood glucose': fasting blood glucose 5.6 – 6.9 mmol/l.
Polygenically determined types of diabetes:
- diabetes mellitus type 1 – autoimmune destruction of β-cells;
- the most severe form of diabetes;
- vitally dependent on insulin treatment (insulin-dependent);
- the predominant type of DM in children, adolescents and young adults.
- diabetes mellitus type 2
- typical disease of adults and elderly;
- associated with excess weight and rising insulin resistance (insulin-independent), which the own insulin secretion cannot overcome.
Monogenically determined types of diabetes:
- MODY (maturity-onset diabetes of the young)
- neonatal diabetes
- diabetic syndromes
- diabetes mellitus associated with cystic fibrosis
Secondary diabetes:
It is caused by the overproduction of certain hormones or pharmaceuticals; rare in children.[1]
References[edit | edit source]
Related Articles[edit | edit source]
- Diabetes mellitus • Diabetes mellitus in pregnancy • Gestational diabetes mellitus • Newborn of a diabetic mother • Other specific types of diabetes mellitus
- Diabetes mellitus type 1 (endocrinology) • Diabetes mellitus type 1 (biochemistry)
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus (endocrinology) • Type 2 diabetes mellitus (biochemistry) • Type 2 diabetes mellitus (pediatrics)
- Selected biochemical tests in patients with diabetes mellitus
- Complications of diabetes mellitus • Diabetic ketoacidosis
- Diabetes and tumors • Transplantation in diabetology
- Metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance
- Diabetic ketoacidosis/case report
- Diabetic education • Diet for type 1 DM • Diet for type 2 DM • Diabetic foods • Special diabetic diets
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Jump up to: a b c d LEBL, J – JANDA, J – POHUNEK, P, et al. Clinical Pediatrics. 1. edition. Galen, 2012. 698 pp. pp. 208-215. ISBN 978-80-7262-772-1.