Tumors
From WikiLectures
Definition: A tumor is a collection of cells growing independently without the control of the organism. Its autonomy is not complete. Blood supply is necessary (size up to 1.5 mm diffusion nutrition, then the tumor needs a vascular supply), hormonal influences or RF.
Morphological characters[edit | edit source]
- Organ enlargement.
- Growths.
- Non-healing ulcer.
- Hardness.
The tumor differs from its surroundings in color, consistency, and surface. Epithelial tumors tend to be grey-white, mesenchymal tumors are pink.
Dividing Tumors[edit | edit source]
Division according to affected tissue[edit | edit source]
- Mesenchymal tumors - arise from mesenchyme. We include tumors of Tissue, Vessel, blood cells, fat cells and muscle cells.
- Epithelial tumors - this includes tumors of the covering, surface and glandular epithelium.
- Neuroectoderm tumors - originating from cells of neuroectoderm origin (CNS tumors, Peripheral nerve tumors and [[melanocyte] ]y).
- Embryonal tumors - this includes germline and organ-specific tumors.
Division by behavior[edit | edit source]
- False tumors - pseudotumors.
- Hypertrophy.
- Hyperplasia.
- Cyst.
- Inflammatory pseudotumor (Schloffer tumor).
- Hamarcia – tissue not involved in the structure of an organ.
- Choristia - clusters of cells in abnormal locations.
- True Tumors
- Benign (non-malignant) – they are capable of differentiating into cells morphologically and functionally similar to the cells from which a benign tumor arises. They do not tend to metastasize - to establish daughter foci, growth is limited, but can restrict surrounding tissues. They are similar to the original tissue, encapsulated and bounded by the ligament of the original tissue. It usually does not cause serious disorders to the wearer. Easily removable surgically. They are marked with the suffix -OM.
- Intermediate (semimalignant) - on the border between malignant and benign tumors, they can form metastases.
- Malignant (malignant) - has a wide spectrum of differentiation - from primitive cells to fully mature. By growth, it destroys surrounding tissues, establishes metastases. Its microscopic structure is similar to immature tissue. Its boundary is difficult to determine.
- Mesenchymal - sarcomas.
- Epithelial - carcinomas.
Speech Types[edit | edit source]
- The tumor does not affect the body's function at all (nevus, lipoma), it can be aesthetically disturbing
- Obstructs the lumen of a hollow organ (resulting in obstructive icterus, ileus, hydronephrosis), narrows the lumen by external pressure, suppresses hematopoiesis (leukemia, [[Molecular mechanisms of metastasis|metastases] ])
- Produces hormones (pheochromocytoma, pituitary adenoma, carcinoid)
- It destroys the environment, fistulas form, infection
- Disrupts vessels
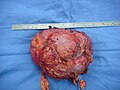
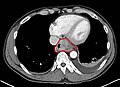
Examples of tumor findings[edit | edit source]
Links[edit | edit source]
Related Articles[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- STŘÍTESKÝ,, Jan,. Patologie. 1. edition. 2001. ISBN 80-86297-06-3.
- WIKIPEDIA,. Nádor [online]. [cit. 2010-11-14]. <https://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/cancer>.